Figure 1.
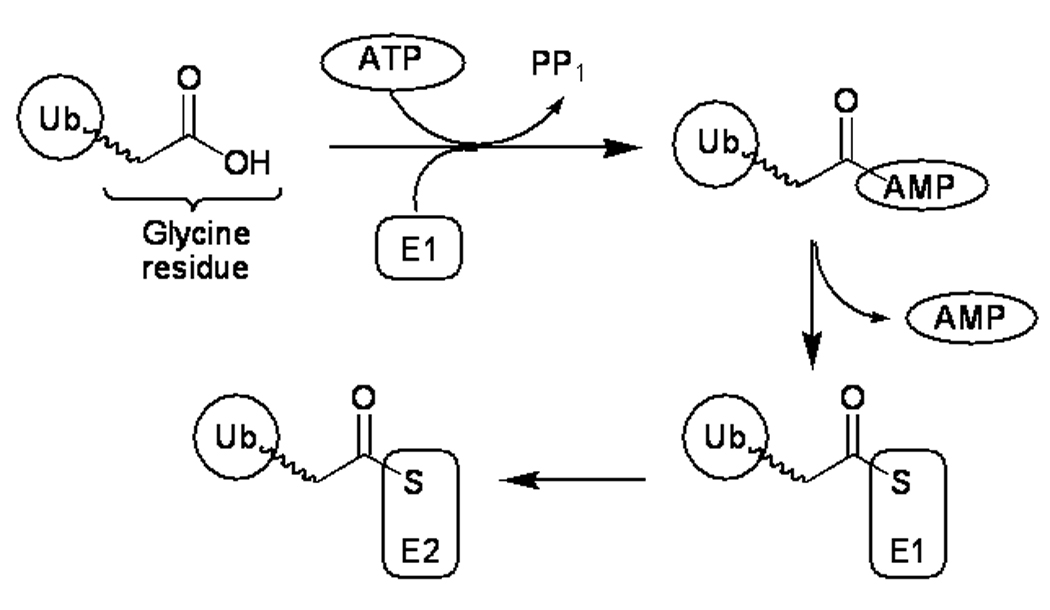
Schematic overview of the role of ubiquitin-activating enzyme, E1. The E1 reaction sequence begins with adenylation of a free ubiquitin molecule with concomitant ATP hydrolysis. The adenylated ubiquitin is then transferred to the active site cysteine residue of E1, followed by transfer to the active site cysteine residue of an E2 ubiquitin ligase, the next enzyme in the catalytic chain.
