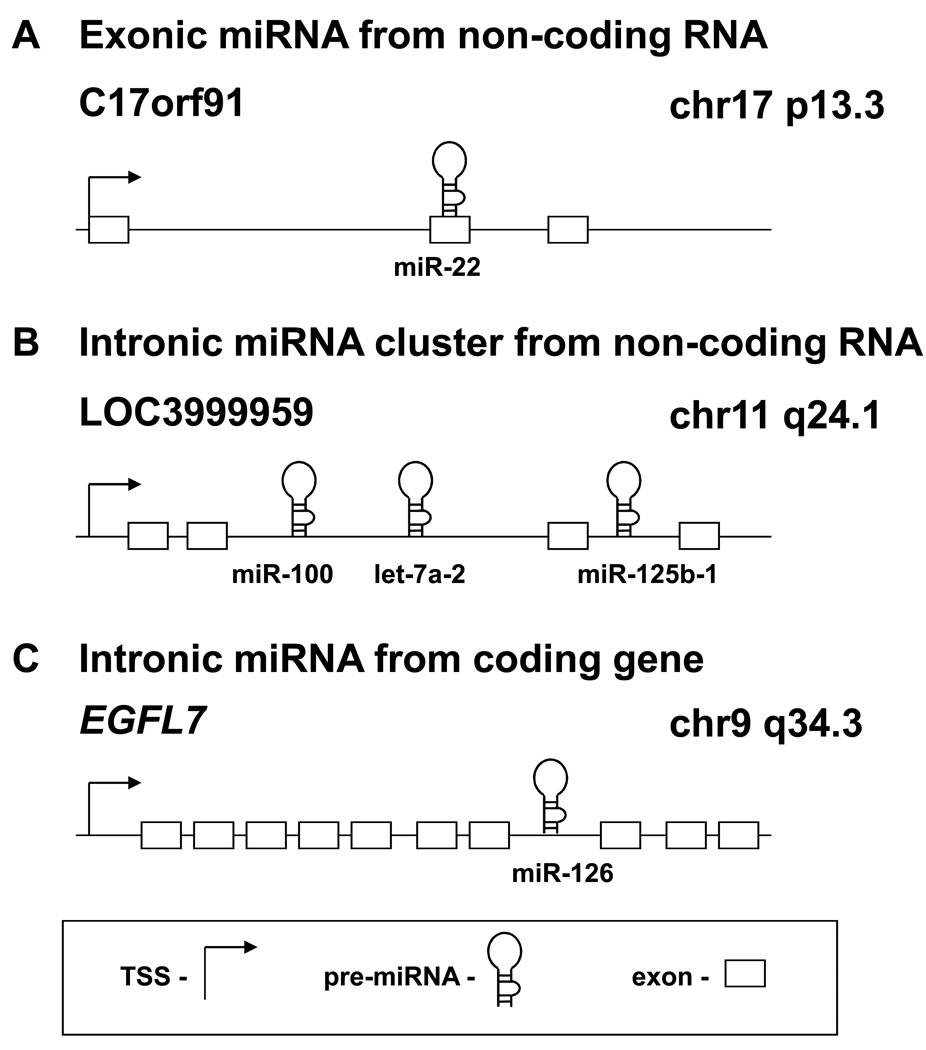
Figure 1.
Genomic locations of miRNAs. miRNAs may be located in almost any region of the genome including repeats. They may be grouped into clusters or situated alone, and may be exonic or intronic. A, a miRNA may be part of the exon of a non-coding RNA transcript, such as miR-22. B, polycistronic miRNAs may be grouped into a cluster and transcribed as a pri-miRNA, which yields several miRNAs. This occurs with the miR-100/let-7a-2/miR-125b-1 cluster, which is transcribed as an intron of a non-coding RNA. C, miRNAs may be located in the introns of canonical genes. The mature miRNA may be processed from the intron of the host gene transcript. This occurs when miR-126 is processed from the EGFL7 transcript. Arrow, transcription start site; hairpin, pre-miRNA; rectangle, exon.