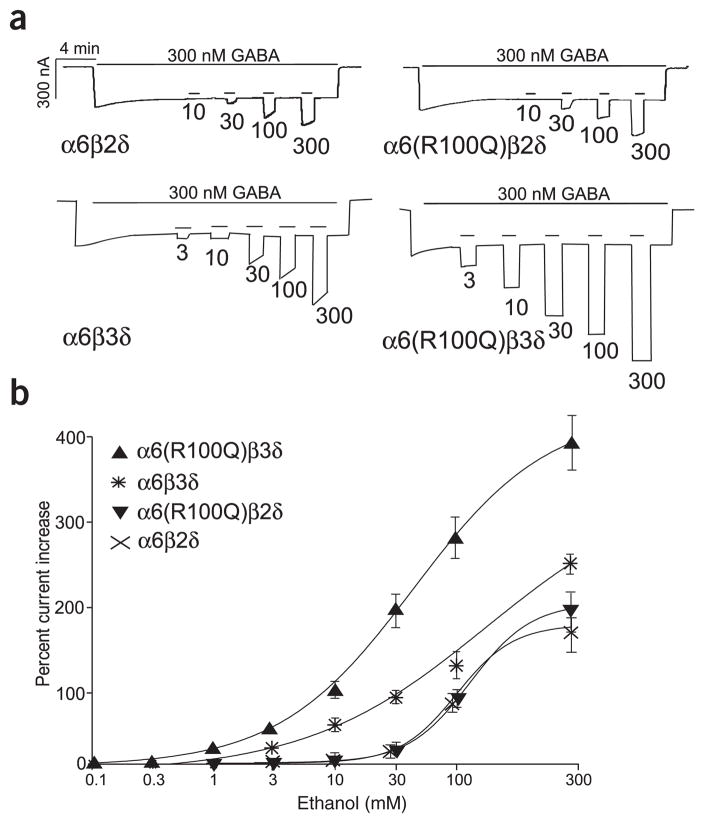
Figure 1.
The α6-R100Q polymorphism leads to a marked increase in ethanol sensitivity when expressed with β3 and δ subunits. (a) GABARs of the indicated subunit compositions were expressed in X. laevis oocytes and activated by steady-state GABA (300 nM ~EC30). Brief applications of ethanol at the indicated concentrations (in mM) enhance the current in a dose-dependent manner. (b) Dose-response curves for ethanol showing the peak enhancement of GABA current. Shown are wild-type and mutant versions of subunit combinations that are likely to be responsible for tonic GABA current in granule cells: α6β2δ (cross, n = 6), α6β3δ (asterisk, n = 10), α6(R100Q)β2δ (inverted triangles, n = 7) and α6(R100Q)β3δ (upright triangles, n = 8). Note that the β3 and δ subunits are required for the R100Q mutation to exert an effect and that replacement of β2 with β3 leads to an almost tenfold increase in ethanol sensitivity. Other combinations of subunits expressed in granule cells are summarized in Table 1.