Figure 1. Hyperosmotic stress and extracellular cAMP stimulus induce VASP phosphorylation in a different manner.
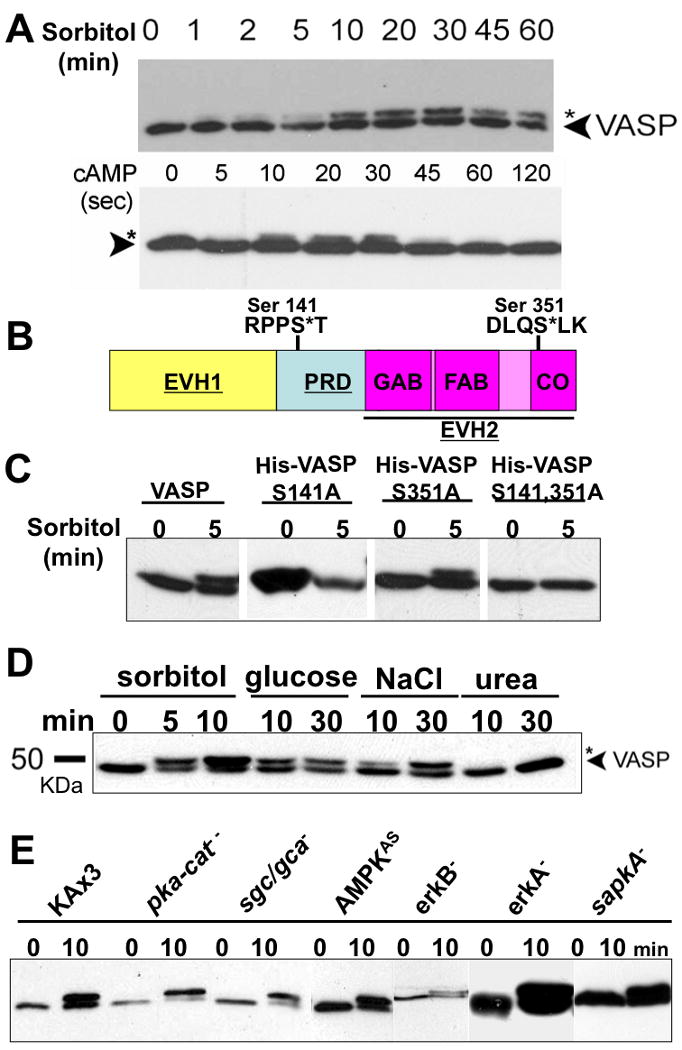
A, Vegetative and KAx3 cells pulsed 5-hrs (5×106/ml) were treated with hyperosmotic shock (0.4M sorbitol, 430 mOsm) and cAMP (100 μM), respectively. Whole cell lysates were taken at different time points as indicated. Samples were subjected to 8% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting probed with VASP antibody. B, Schematic diagram of Dictyostelium VASP. PRD (proline-rich domain) is flanked by EVH1((Ena/VASP homology 1) and EVH2 domains. EVH2 domain, indicated with underline, harbors G-actin binding (GAB), F-actin binding (FAB), and coiled-coil (CO) regions. Two putative phosphorylation motifs (Ser-141 and Ser-351) on VASP are shown. C, 6× His-tagged VASP phosphorylation mutants (S141A, S351A, and S141A/S351A) were expressed in vasp null background and stimulated with sorbitol. Phosphorylation of VASP was examined by immnoblotting after SDS-PAGE. D, Examination of VASP phosphorylation caused by different hyperosmolarity-inducing agents. Cells were exposed to hyperosmotic shock generated by different reagents as indicated for different period of time. E, null (pka-cat-, sgc/gca-, erkA-, erkB-, sapkA-) and antisense (AMPKAS) cells were treated with sorbitol for 10 min. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting probed with anti-DdVASP antibody.
