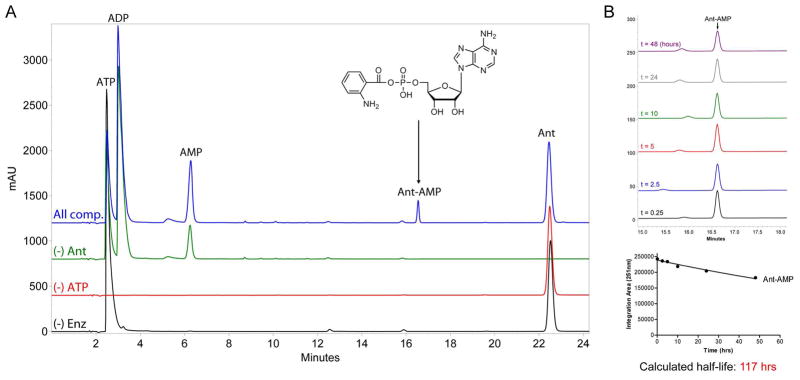
Figure 7.
HPLC-based determination of anthranilyl-AMP formation by AFUA_6g12080 module 1 C*AT and stability of Ant-AMP following release from enzyme. (A) Overlay of HPLC chromatograms (251 nm detection) obtained from 20 μL injections of control (black, red, and green traces) and experimental (blue trace) reactions monitoring the in vitro adenylation activity of C*AT with anthranilic acid as substrate. All reactions contained 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM DTT; and varied combinations of 10 μM C*AT (“Enz”), 5 mM ATP, and 1 mM Ant as indicated. The chemical identity of peaks was determined by running authentic standards and high-resolution mass spectrometry. (B) The stability of Ant-AMP in reaction buffer following release from enzyme. Top image, overlay of HPLC chromatograms (251 nm detection) obtained at different timepoints post microcentrifugal filtration (10K molecular weight cutoff) of a sample prepared similar to the “All components” reaction presented in panel (A). Bottom image, quantification of Ant-AMP peak area for each timepoint used for determination of Ant-AMP stability in terms of calculated half-life.