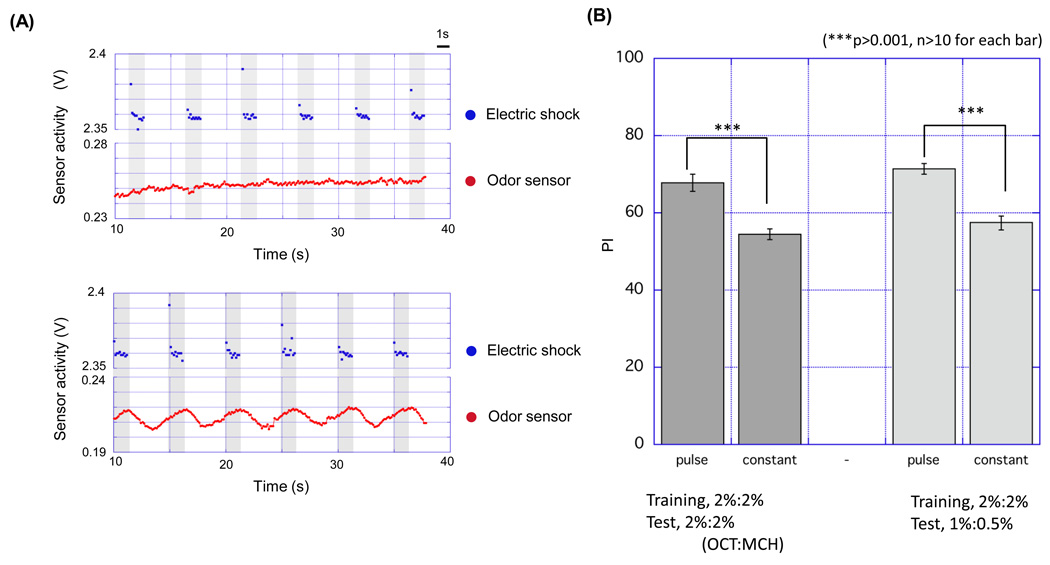
Figure 4. Pulsed odor-flow improved learning score.
(A) Plots of odor sensor activity (red dots) and electric shock (blue dots) measured during the training. Airflow containing an odorant was delivered constantly (upper panel) or in pulses (bottom panel) to the training tube, which is accompanied 12 times with 1.5 s periodic electric shocks. In the pulsed flow protocol, electric shock presentations start after the rising of odor concentration and stop immediately before the falling of odor concentration. To generate the pulsed flow, a valve connected to an odor cup was opened for 3 s, followed by opening of a valve for 2 s that is connected to a cup containing mineral oil. (B) PI of flies trained by pulsed or constant flow. PI was examined 3 min after the training. Pulsed flow gave a higher PI than constant flow (n=10, p** < 0.01, t-test). Data are presented as mean ±SEM.