Figure 4.
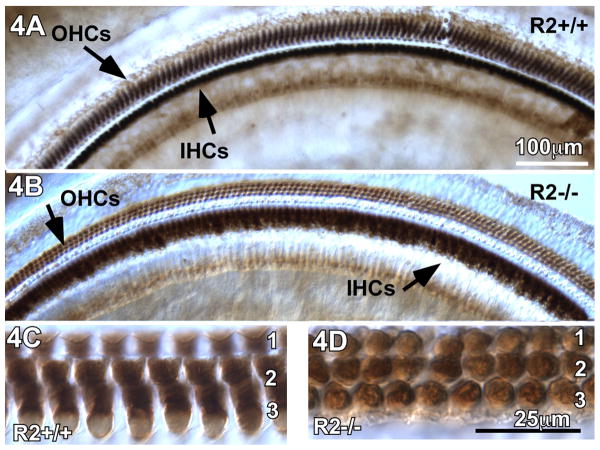
Loss of CRFR2 activity does not result in structural pathology of the organ of Corti in mice that were born and raised in quiet ambient sound environment and moved to a moderately noisy ambient sound environment. 4A- Calbindin immunostaining of wild type cochleae reveal intense labeling of the OHCs and IHCs along the entire length of the cochlea. 4B- Calbindin immunostaining of CRFR2-/- cochleae also revealed immunostaining of OHCs and IHCs. While the IHCs were stained, they were not as intensely immunoreactive as observed in wild types. Additionally, the OHCs were only lightly immunoreactive compared to wild types. However, there was no evidence of OHC or IHC loss in the CRFR2-/- mice. 4C,D- Higher magnification of the outer hair cells reveals differences in the cellular localization of calbindin between wild type (C) and CRFR2-/- (D) mice. In wild type mice, immunostaining is observed throughout the cytoplasm of the hair cells, leaving the nuclei blank. In mice lacking CRFR2, the majority of calbindin immunostaining in OHCs is observed at the nuclear level.