Fig. 4.
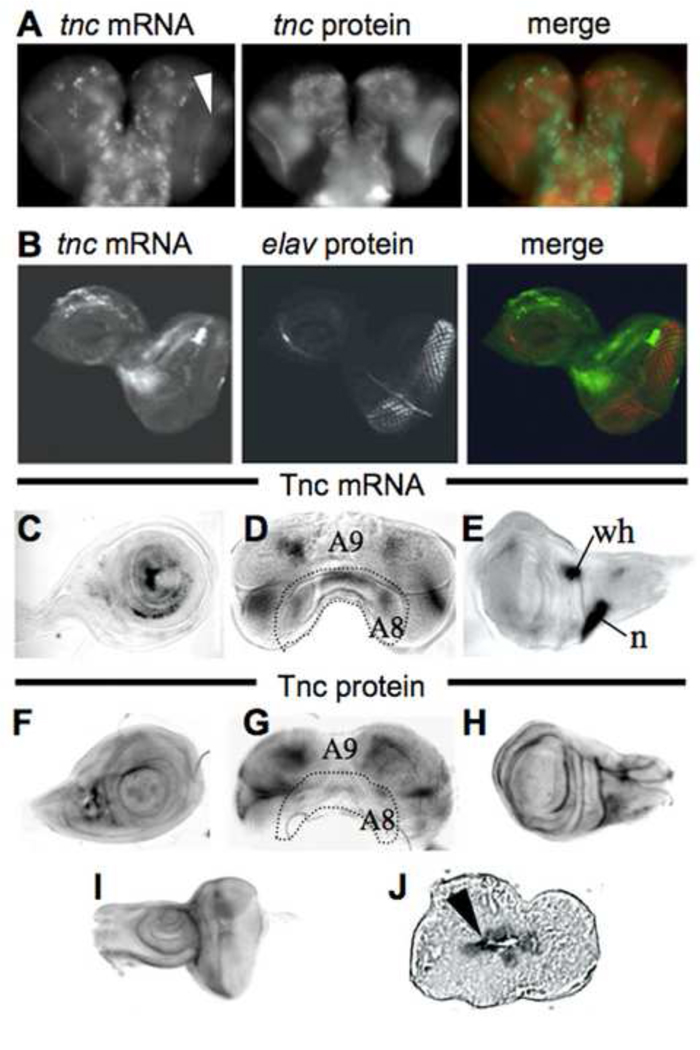
tenectin is expressed in brain and imaginal discs during post-embryonic development. tenectin nucleic acid or antibody probes were hybridized to brain and discs dissected from late third instar larvae (A–I). Brain (A) and eye-antennal disc (B) stained for tenectin transcript (green) and tenectin protein (red: A) or elav protein (red: B). Cells of the optic lobes corresponding to the lamina region expressing tenectin transcripts are indicated (arrowhead in A). Leg (C), male genital (D) and wing (E) discs probed for tenectin transcript. Leg (F), male genital (G) wing (H) and eye-antennal discs (I) probed for tenectin protein. Prepupal wing disc, transversal cut, stained for tenectin protein (J) showing its localization to the apposed surfaces of the dorsal and ventral wing layers (arrowhead). Regions of the male genital discs corresponding to different abdominal segment cells (Casares et al., 1997) are indicated (D and G). n: notum; wh: wing hinge.