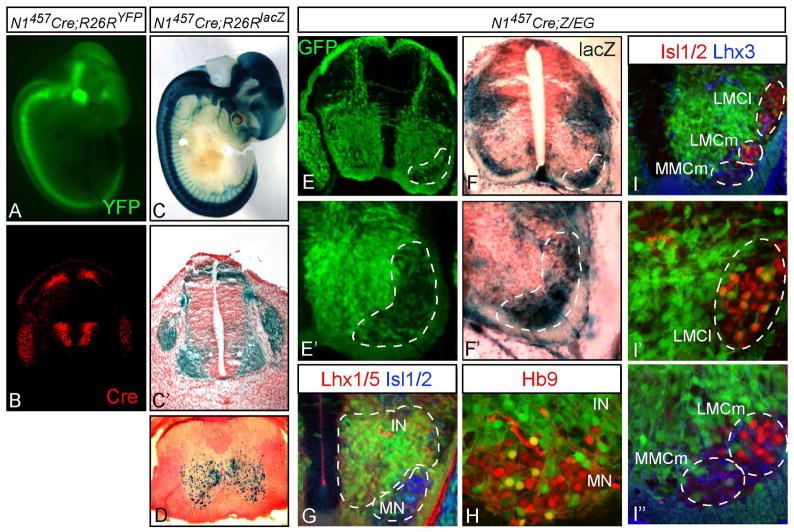
Figure 5. In vivo analysis of the Neurog1 lineage in the neural tube using Cre recombinase.
(A,C) E11.5 embryos from N1457-Cre crossed with Cre reporter strains are shown in whole mount (A, R26RYFP; C, R26RlacZ), or cross section (C′). (B) Cre immunofluorescence mimics the Neurog1 pattern in the neural tube at E11.5 (compare to Fig. 3A). (D) spinal cord from a 30-day old N1457-Cre;R26RlacZ mouse showing the location of Neurog1-lineage neurons. (E-I) Cross sections through the neural tube of N1457-Cre;Z/EG E12.5 embryos. (E,E′) GFP shows Neurog1 lineages where Cre activity has recombined the reporter and includes the drg, a minor dorsal population, and a major ventral population in the neural tube. (F,F′) X-gal staining indicates non-Neurog1 lineages that lack Cre activity. The dashed area highlights motoneuron populations that are mostly not included in the Neurog1 lineages. (G) extensive co-expression of the GFP is detected with the broad interneuron (IN) marker Lhx1/5. (H,I) co-expression with motoneuron (MN) markers Hb9, Isl1/2, and Lhx3 is low. LMCm, lateral motor column medial; LMCl, lateral motor column lateral; MMCm, medial motor column medial.