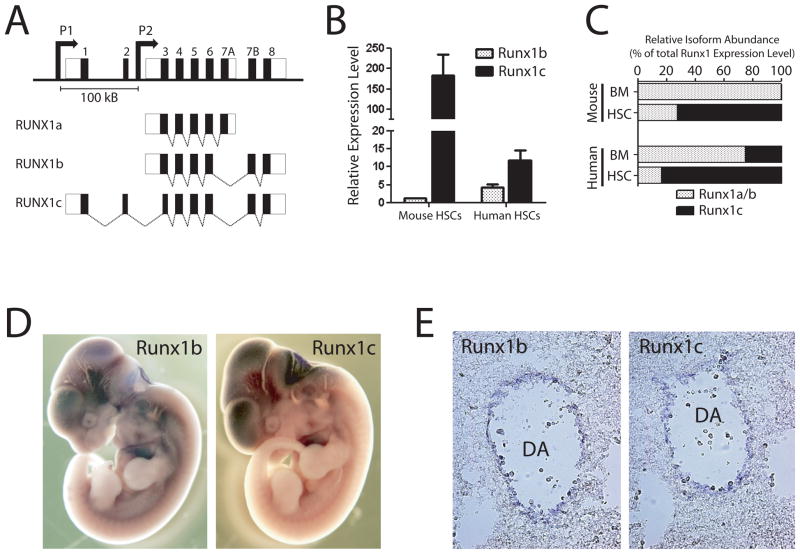
Figure 1.
RUNX1 genomic locus and isoform expression patterns. (A) Genomic organization of human RUNX1 locus. The RUNX1c isoform is transcribed from the distal P1 promoter and contains the unique N-terminal amino acids encoded by exons 1 and 2. The RUNX1a and predominant RUNX1b isoforms are transcribed from the proximal P2 promoter. The promoters are separated by over 100 Kb in the genome. (B) Expression of RUNX1 isoforms in hematopoietic stem cells. Real-time PCR analysis showed that the RUNX1c isoform is much more highly expressed in HSCs compared to RUNX1b relative to whole bone marrow in both human and mouse. (C) Relative abundance of RUNX1c versus RUNX1a and RUNX1b isoforms in mouse and human bone marrow (BM) and HSCs calculated as a proportional ratio of total RUNX1 expression level. These data show that the RUNX1c isoform is much more abundant in HSCs compared to whole BM. (D) Wholemount in situ hybridization analysis of Runx1 isoform expression patterns in E11.5 mouse embryos. On a gross level, the expression patterns of Runx1 isoforms at this stage of mouse development were highly overlapping. (E) Sectioning of stained embryos showed that Runx1b and Runx1c were both expressed in the endothelium lining the dorsal aorta in the AGM region where definitive HSCs are born.