Figure 2. Feedback loops modulating mTOR signaling pathway.
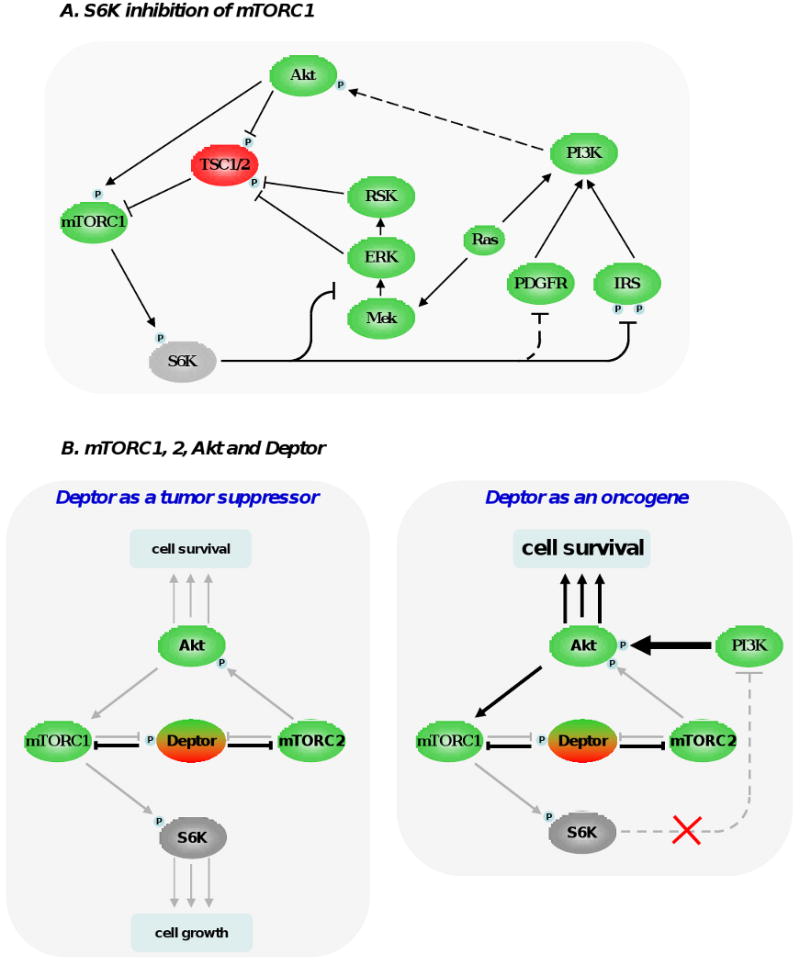
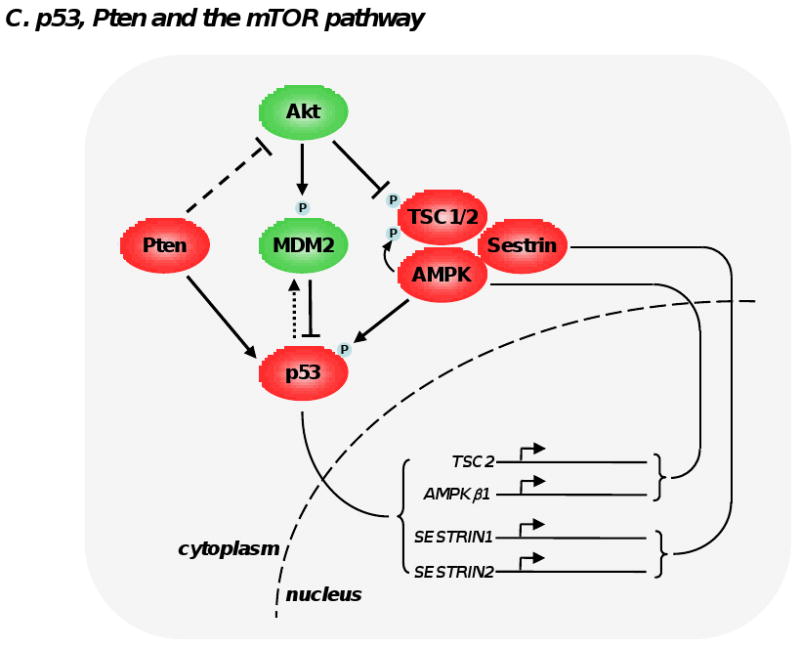
(A) S6K1 phosphorylation by mTORC1 triggers a number of feedback loops that negatively impact on PI3K signaling. S6K1 directly phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) at multiple sites, which leads a significant attenuation of insulin and and insulin-like growth factor effect at the cell membrane. S6K1 also inhibits PDGFR and the MEK/ERK signaling pathway through a not fully-understood mechanism. These 3 inhibitory loops ultimately dampen PI3K, Akt and mTORC1 activation and have likely evolved as a cellular response to buffer aberrant or excessive PI3K activity. (B) Deptor can have oncogenic and tumor suppressive properties. By blocking mTORC1 and mTORC2, Deptor inhibits protein synthesis, cell size increase and the proliferative and survival effects of Akt. However, under certain conditions, inhibition of mTORC1 by Deptor relieves the feedback inhibition from S6K1 to PI3K, boosting Akt activity. (C) The 2 most important tumor suppressors, namely Pten and p53, cooperate in the inhibition of mTORC1. p53 transactivates many negative regulators of mTORC1 (TSC2, AMPKβ1, Sestrin 1 and 2), which oppose Akt activity. Akt favors degradation of p53 by phosphorylating and stabilizing MDM2. Importantly, Pten and AMPK directly stabilize p53. Collectively, these interactions imply the existence of a coordinate regulation of mTOR signaling pathway by energy, nutrients, growth factors, oncogenic stress and DNA integrity.
