Figure 7.
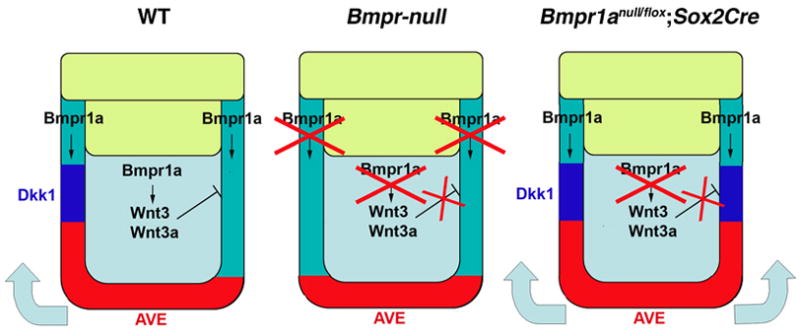
Models of how BMP signaling through BMPR1A regulates anterior movement of the AVE through Dkk1 expression
Our model describing the function of BMP signaling through BMPR1A in the early mouse embryo in regulating AVE migration. (WT) BMP signaling in the VE induces Dkk1 expression in the PxVE circumferentially. On the other hand, BMP signaling in the epiblast induces Wnt3 and Wnt3a expression in the epiblast to inhibit Dkk1 expression in majority of the PxVE except for a most anterior domain. The resulting anterior expression of Dkk1 induces anterior migration of the AVE. (Bmpr-null) In Bmpr-null embryos, Dkk1expression is downregulated (or not induced) in PxVE, resulting in lack of AVE migration. (Bmpr1anull/flox; Sox2Cre) In the embryos lacking Bmpr1a in an epiblast-specific manner, Wnt3 and Wnt3a are both downregulated and circumferential Dkk1 expression remains in the PxVE. Thus, the AVE cells migrate bilaterally toward PxVE. In both cases, embryos fail to establish a normal A-P axis due to the abnormal migration of the AVE (no migration in Bmpr-null embryos, random migration in Bmpr1anull/flox; Sox2Cre embryos).
