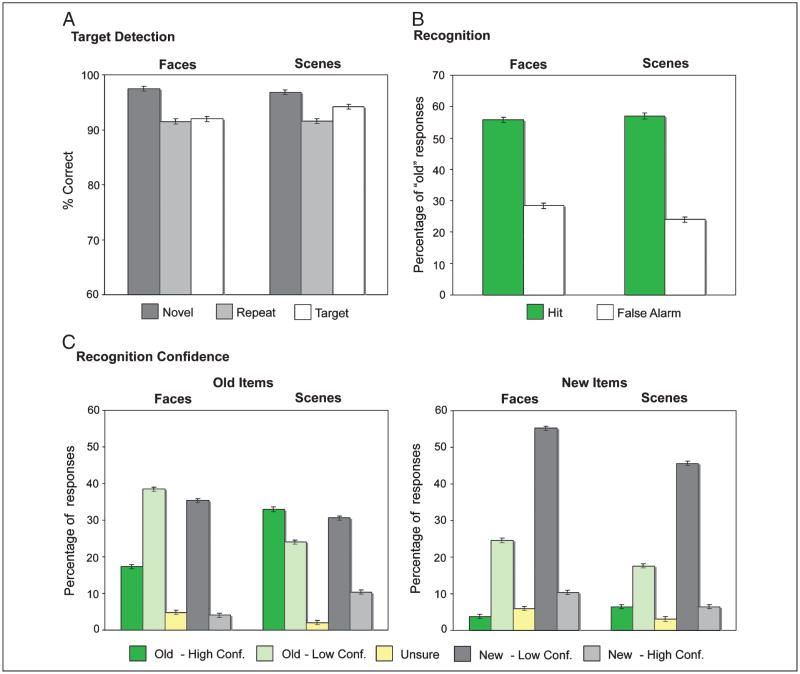
Figure 2.
Behavioral performance. (A) Target detection accuracy during scanned encoding for novel (dark gray), repeated (light gray), and target (white) stimuli. (B) Percentage of “old” responses on the recognition memory task collapsed across confidence for face and scene stimuli. Hits (green) and false alarms (white) are plotted separately for each stimulus class. (C) Percentage of responses on the recognition memory task for old and new items by level of confidence for face and scene stimuli. High-confidence “old” responses (dark green), low-confidence “old” responses (light green), “unsure” responses (yellow), low-confidence “new” responses (dark gray), and high-confidence “new” responses (light gray) are plotted separately for each stimulus class.