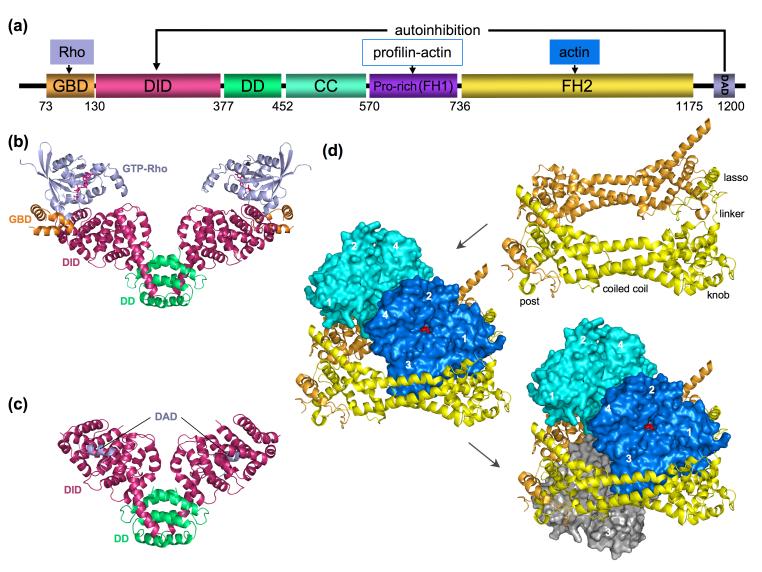
Figure 1.
Domain diagram of DRFs and representative structures. (a) A prototypical DRF (domain boundaries correspond to mDia1) consists of the following domains: GBD (GTPase-binding domain), DID (diaphanous inhibitory domain), DD (dimerization domain), CC (coiled coil), FH1 and FH2 (formin homology 1 and 2 domains) and DAD (diaphanous autoregulatory domain). (b-c) Structures of N-terminal regulatory fragments with bound RhoC [9] and DAD [10]. Ribbon diagrams colored according to the domain diagram in part a. (d) Illustrations of the structure of the FH2-actin complex [12] showing, in a sequence, the crystallographic FH2 dimer (obtained after domain swapping the ‘lasso’ region from the lower subunit), the actin subunits bound to the dimer (blue and cyan), and a third actin from the complex below (gray). Each FH2 domain is structurally subdivide into lasso, linker, knob, coiled coil and post regions. This figure is inspired by similar figures in [3].