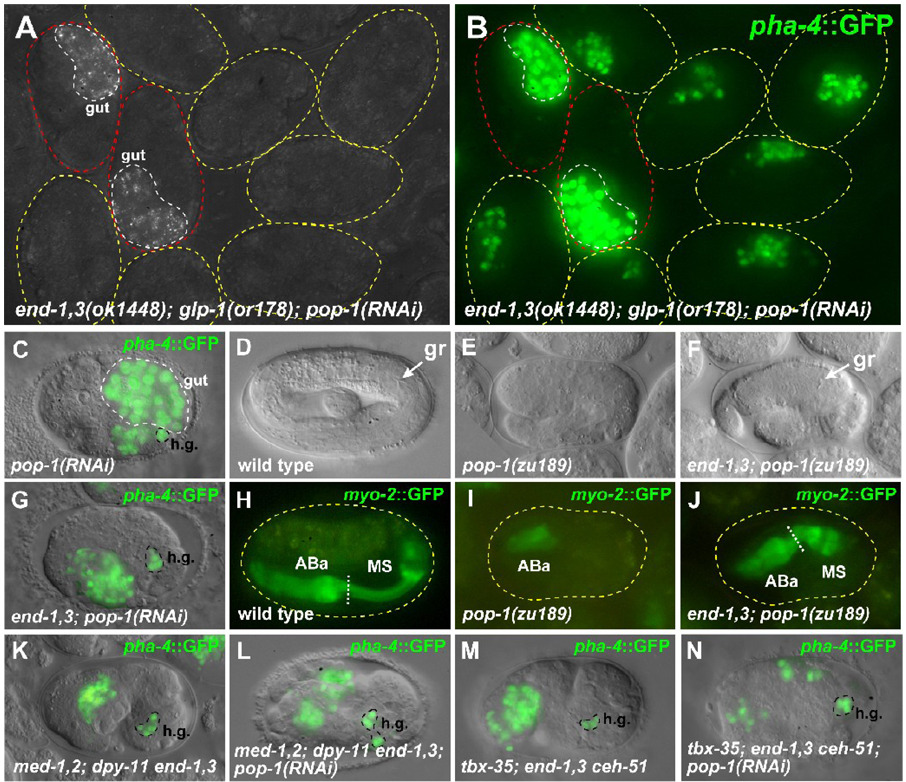
Fig. 3.
Embryos lacking end and pop-1 function make MS-type pharynx. (A) Polarized light image of a field of end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448); glp-1(or178ts) embryos raised at the non-permissive temperature for or178 and treated with pop-1(RNAi). The two embryos on the left (outlined in red) carry an end-1,3(+) transgene and are the only embryos making gut. (B) Fluorescence image of the same embryos in panel A showing pha-4::GFP expression (Horner et al., 1998; Kalb et al., 1998). Expression in the two rescued embryos (red outline) is from gut cells, while in the remaining embryos expression is from GLP-1-independent pharynx cells (an average of 16.8 ± 1.1 cells, n=93). We do not observe the rectum component of pha-4::GFP expression in our glp-1(or178) strain when it is raised at 25°C (data not shown). (C) GFP overlay of pha-4::GFP expression in a pop-1(RNAi) embryo. The bright signals in large nuclei are gut nuclei (confirmed by polarized light birefringence), while the remaining expression is from hindgut cells (h.g.) and ABa-derived pharynx (an average of 21.3 ± 0.8 cells, n=18). (D) Elongated wild-type embryo with grinder (gr) indicated. (E) Arrested pop-1(zu189) dpy-5(e61) embryo from pop-1 dpy-5 mother. (F) Arrested end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448); pop-1(zu189) dpy-5(e61) embryo from an end-1,3; pop-1 dpy-5 mother rescued by an end-1,3(+) transgene. The grinder (gr) within a posterior pharynx-like structure is indicated. (G) Expression of pha-4::GFP in an end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448); pop-1(RNAi) embryo in hindgut (h.g.) and pharynx (average of 44.8 ± 2.2 pharynx cells, n=17). (H–J) myo-2::GFP expression (Okkema et al., 1993) showing presence of ABa- and MS-derived portions of pharynx in wild-type (H) and end-1,3; pop-1 (J) embryos, but lacking MS-derived pharynx in a pop-1 mutant (I). (K–N) pha-4::GFP expression in chromosomal mutant backgrounds that block MS specification, with and without pop-1(RNAi). (K,L) med-1(ok804); med-2(cx9744); dpy-11(e224) end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448) background. (M,N) tbx-35(tm1789); end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448) ceh-51(tm2123) background. In these mutant backgrounds, the number of pha-4::GFP-expressing cells is actually reduced from ~30 to ~22 when pop-1(RNAi) is added, owing to an apparent requirement for pop-1 in ABa-derived pharynx (Table 2). An additional requirement for pop-1 in morphogenesis (Lin et al., 1998) results in dispersal of pha-4::GFP-expressing cells in panels L and N. Embryos in most panels have been oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal up.