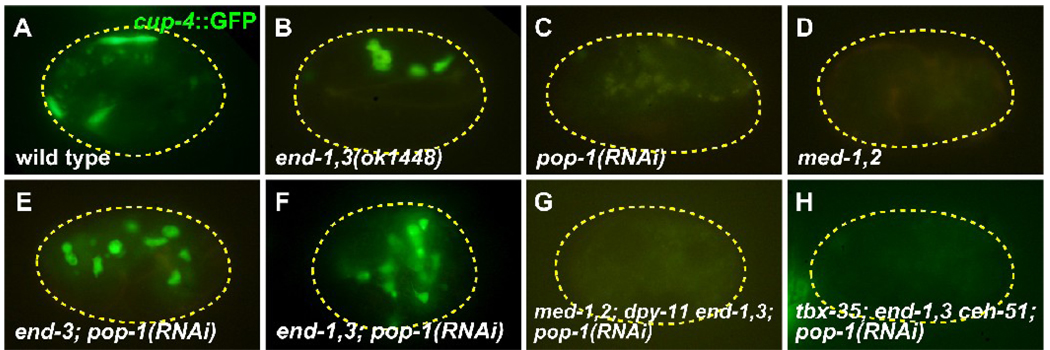
Fig. 4.
Coelomocytes are made in end-1,3; pop-1 mutant embryos. All embryos carry a cup-4::GFP coelomocyte-specific marker (Patton et al., 2005). (A) Wild-type embryo showing accumulation of cup-4::GFP expression in four coelomocytes (the top two are adjacent). (B) Normal coelomocytes in an end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448) mutant. (C,D) Loss of coelomocytes in pop-1(RNAi) and med-1(ok804); med-2(cx9744) embryos, in which a penetrant mis-specification of MS occurs (Broitman-Maduro et al., 2009; Lin et al., 1995; Maduro et al., 2001). (E,F) Supernumerary coelomocytes are made in end-3(ok1448); pop-1(RNAi) embryos (average of 6.1 ± 0.2 cup-4::GFP expressing cells, n=77) and end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448); pop-1(RNAi) embryos (average of 10.7 ± 0.3 cells, n=77). (G,H) Loss of coelomocytes in med-1(ok804); med-2(cx9744); dpy-11(e224) end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448); pop-1(RNAi) and tbx-35(tm1789); end-1(ok558) end-3(ok1448) ceh-51(tm2123); pop-1(RNAi) embryos. Faint yellow signal in some panels corresponds to gut granules.