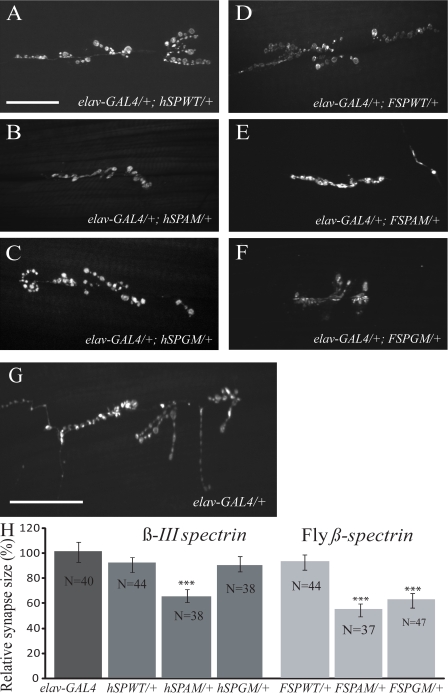
Figure 3.
Spectrin mutations affect synaptic terminal size at the NMJ. (A–G) Confocal fluorescence images of NMJs on ventral longitudinal muscles 6/7 of larval abdominal segments 2 and 3. Larval synapses were visualized by staining with an antibody to the synaptic vesicle–associated protein CSP. Neuronal expression of the hSPAM, FSPAM, and FSPGM transgenes driven by elav-GAL4 results in less NMJ expansion and fewer synaptic boutons and branches (B, E, and F) when compared with the elav-GAL4 driver line (G). Neuronal expression of hSPWT, hSPGM, or FSPWT transgenes did not affect synapse size (A, C, and D). Bars, 50 µm. (H) Quantification of bouton number shows a significant reduction in synapse size (number of synaptic boutons per surface area of muscle 6/7) in larvae expressing the hSPAM, FSPAM, and FSPGM mutant transgenes (***, P < 0.001). Numbers are normalized to elav-GAL4 in the graph. Data are mean ± SEM (error bars).