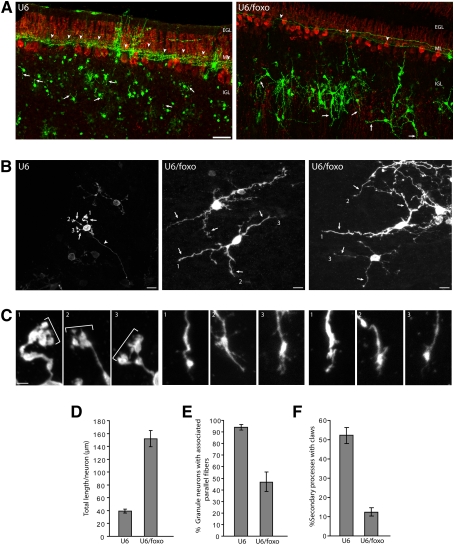
Figure 5.
FOXO knockdown-induced impaired neuronal polarity phenotype in vivo is sustained in later stages of development. (A) P3 rat pups were injected in the cerebellum with the control U6-cmvGFP or U6/foxo-cmvGFP RNAi plasmid and then subjected to electroporation. Nine days, later at P12, pups were sacrificed and coronal sections of cerebella were subjected to immunohistochemistry with the GFP (green) and calbindin (red) antibodies, the latter to label Purkinje cells. In control animals (U6), granule neurons in the IGL were typically associated with parallel fibers. The FOXO knockdown-induced loss of parallel fibers was sustained at this later stage of development (P12). In addition, secondary processes in the IGL (dendrites in control) appeared to be much longer in FOXO knockdown animals as compared with control animals. Arrows and arrowheads indicate dendrites and parallel fibers, respectively. Bar, 50 μm. (B,C) Higher magnification of granule neurons in the cerebellar cortex in animals electroporated and analyzed as in A. The numbered dendritic tips shown in B are magnified in C. Mature dendrites in control animals bear dendritic claws at their ends (indicated by brackets), which represent characteristic post-synaptic structures (Shalizi et al. 2006). In contrast, the aberrant long secondary processes in the IGL in FOXO knockdown animals have tapered ends lacking dendritic claws. Bars: B, 50 μm; C, 10 μm. (D) Quantification of total length of secondary processes in the IGL of granule neurons in animals electroporated and analyzed as in A. FOXO knockdown significantly increased total secondary process length in granule neurons (P < 0.001; t-test, n = 3 brains, 172 neurons measured). (E) Quantification of parallel fiber phenotype upon FOXO knockdown in vivo. The percentage of granule neurons in the IGL that were associated with parallel fibers was significantly reduced in FOXO knockdown animals as compared with control transfected animals (P < 0.01; t-test, n = 3 brains, 809 neurons measured). (F) Quantification of the number of dendritic claws in control and FOXO knockdown animals. FOXO knockdown significantly reduced the number of secondary processes in the IGL (dendrites in control) bearing claws (P < 0.005; t-test, n = 3, 141 neurons measured).