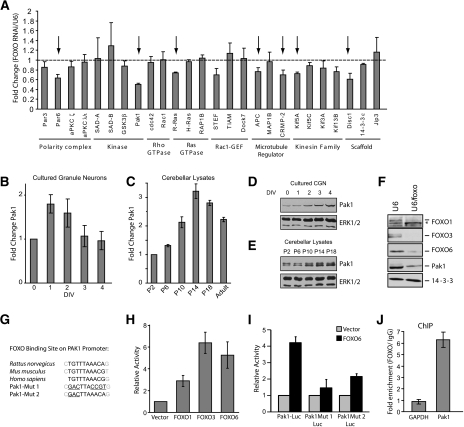
Figure 6.
Identification of Pak1 as a direct target of FOXO transcription factors in neurons. (A) Granule neurons were transfected at high efficiency with the control U6 or U6/foxo RNAi plasmid. Two days later, RNA was extracted and reverse-transcribed for use in quantitative PCR of genes encoding proteins implicated in the establishment of neuronal polarity. Knockdown of FOXO transcription factors significantly reduced expression of several polarity genes. Pak1 expression was the most robustly down-regulated of all of the genes tested. Arrows indicate genes that are significantly reduced in FOXO knockdown neurons as compared with U6 control transfected neurons (P < 0.05; t-test, n = 3). (B,C) Pak1 mRNA abundance was assessed by quantitative RT–PCR in cultured granule neurons (B) or in the cerebellum (C) at the indicated time points. Pak1 mRNA abundance increases preceding the onset of polarization. (D,E) Pak1 protein expression was analyzed by immunoblotting of lysates prepared from cultured granule neurons (D) or from cerebellar lysates (E) at the indicated time points. Pak1 expression increases during the period of polarization. (F) Granule neurons were transfected at high efficiency with the control U6 or the U6/foxo plasmid. Four days later, lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. FOXO knockdown triggered the down-regulation of Pak1 protein levels in neurons. (G) The Pak1 promoter contains putative FOXO-binding sites. Sequence alignment of a fragment of rat, mouse, and human Pak1 promoters is shown along with the engineered mutations in the putative FOXO-binding sites. (H) Granule neurons were transfected with a luciferase reporter gene under the control of a 1.4-kb region of the rat Pak1 promoter containing conserved FOXO-binding sites (Pak1-Luc) and an expression plasmid encoding FOXO1, FOXO3, FOXO6, or the control plasmid, together with a Renilla reporter to serve as control for transfection efficiency. Expression of FOXO transcription factors significantly increased the activity of the Pak1-Luc reporter gene (P < 0.01; ANOVA, n = 3). (I) Granule neurons were transfected with a plasmid encoding FOXO6 or its control vector together with Pak1-Luc or the Pak1 promoter containing mutations within the putative FOXO-binding site (Pak1 Mut 1/2-Luc) and the tk-Renilla reporter. Expression of FOXO6 robustly induced the expression of the Pak1-Luc reporter gene (P < 0.001; ANOVA, n = 3), but failed to effectively induce the expression of the Pak1 Mut 1-Luc or the Pak1 Mut 2-Luc reporter gene. (J) FOXOs occupy the promoter of the endogenous Pak1 gene in granule neurons by ChIP analysis. Granule neuron chromatin was subjected to immunoprecipitation with a control IgG antibody or with antibodies to FOXO1, FOXO3, and FOXO6. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by quantitative PCR using primers designed to amplify the promoter of the Pak1 gene encompassing the putative FOXO-binding sequence or the first exon of the GAPDH gene as control. Data are plotted as the relative FOXO/IgG immunoprecipitation efficiency. FOXO occupancy at the Pak1 gene is significant relative to the GAPDH gene (P < 0.005; t-test, n = 3).