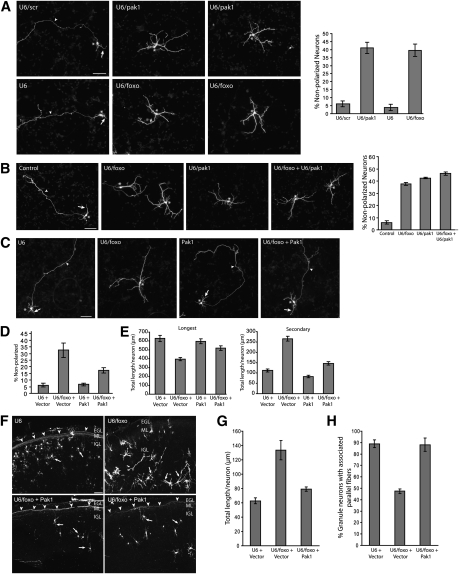
Figure 7.
The polarity-associated protein kinase Pak1 mediates FOXO-dependent neuronal polarity. (A) Granule neurons transfected with the control U6, U6/foxo, U6/scr, or U6/pak1 RNAi plasmid and the GFP expression plasmid were subjected 4 d after transfection to immunocytochemistry with the GFP antibody. Knockdown of Pak1 significantly increased the number of nonpolarized neurons as compared with control U6/scr (P < 0.0001; ANOVA, n = 3) and phenocopied FOXO knockdown. Bar, 50 μm. (B) Granule neurons were transfected with the control U6, U6/foxo, or U6/pak1, or both the U6/foxo and U6/pak1 RNAi plasmids, together with the GFP expression plasmid and subjected to immunocytochemistry 4 d later. While individual Pak1 or FOXO knockdown increased the number of nonpolarized neurons (P < 0.0001; ANOVA, n = 3), simultaneous FOXO and Pak1 knockdown did not additively increase the number of nonpolarized neurons as compared with Pak1 knockdown. (C) Granule neurons transfected with the control U6 or U6/foxo RNAi plasmid together with a plasmid expressing Pak1 or its control vector and the GFP expression plasmid were subjected 4 d after transfection to immunocytochemistry with the GFP antibody. (D) Expression of Pak1 significantly reduced the percentage of nonpolarized neurons in the background of FOXO RNAi (P < 0.01; ANOVA, n = 3). (E) Morphometric analysis shows that the length of the longest process (axon in control) was significantly reduced and the length of secondary processes (dendrites in control) was significantly increased upon FOXO RNAi (P < 0.0001; ANOVA, n = 3). Pak1 expression in the background of FOXO RNAi significantly increased the length of the longest process and significantly reduced the length of secondary processes as compared with FOXO RNAi alone (P < 0.001; ANOVA, n = 3). A total of 636 neurons were measured. (F–H) Coronal sections of P8 rat pups electroporated at P3 with the control U6-cmvGFP or U6/foxo-cmvGFP RNAi plasmid together with the Pak1 expression plasmid or its control vector were subjected to immunohistochemistry with the GFP antibody. Expression of Pak1 in the background of FOXO knockdown in vivo significantly reduced the length of secondary processes in the IGL (P < 0.05; ANOVA, n = 3) and significantly increased the number of parallel fibers associated with IGL granule neurons (P < 0.01; ANOVA, n = 3) as compared with FOXO knockdown animals. Arrows and arrowheads indicate dendrites and parallel fibers, respectively. Bar, 50 μm.