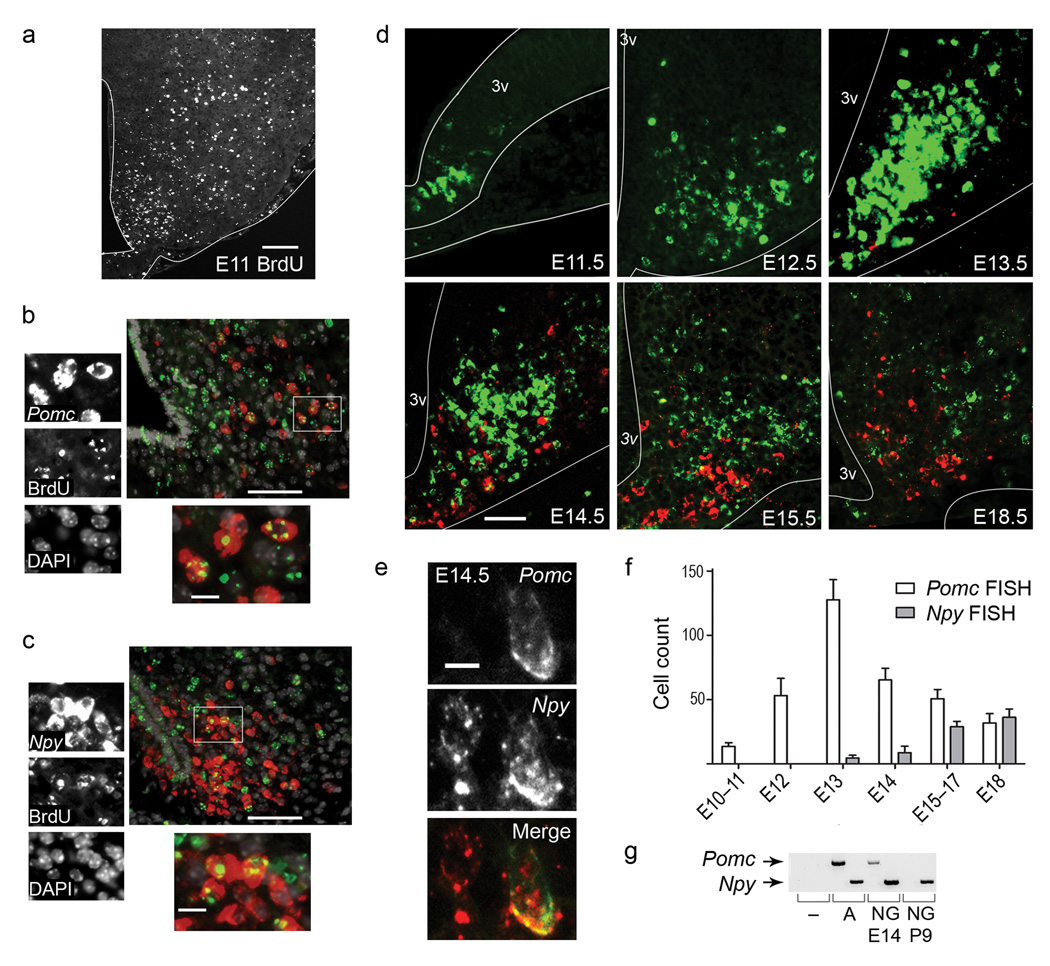
Figure 1.
Pomc is transiently expressed in a broad population of hypothalamic neurons during embryonic development. (a–c) We injected wild-type dams once with 200 mg kg−1 BrdU at E11.5 and sacrificed the offspring at P9 for analysis. (a) BrdU IHC. (b,c) Combined FISH with IHC using probes against Pomc (b) or Npy (c) in conjunction with an antibody against BrdU and counterstained for DAPI. Magnified view of boxed area to the left and below. (d) FISH for Pomc (green) and Npy (red) in ventral hypothalamus from E11.5–E18.5. (e) Confocal image of a cell containing both Npy and Pomc transcripts at E14.5. (f) We counted cells expressing Pomc and Npy as described in Supplementary Fig. 3. Each group represents the average counts of at least 5 coronal sections per animal spanning the rostrocaudal extent of the presumptive ARH with error bars representing mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3 animals for each group). (g) We dissociated cells from transgenic Npy-hrGFP hypothalami and FACS-purified GFP+ cells at E14.5 and P9. Pomc and Npy expression, as assessed by PCR on cDNA generated from sorted GFP+ cells. Abbreviation for sources of cDNA: no cDNA control (−); adult hypothalamus positive control (A); Npy-hrGFP (NG). 3V, third ventricle; Scale bar (a) 100 µm, (b,c) low mag 50 µm, high mag 10 µm (d) 50 µm, (e) 5 µm; all tissue 10 µm cryo-sections.