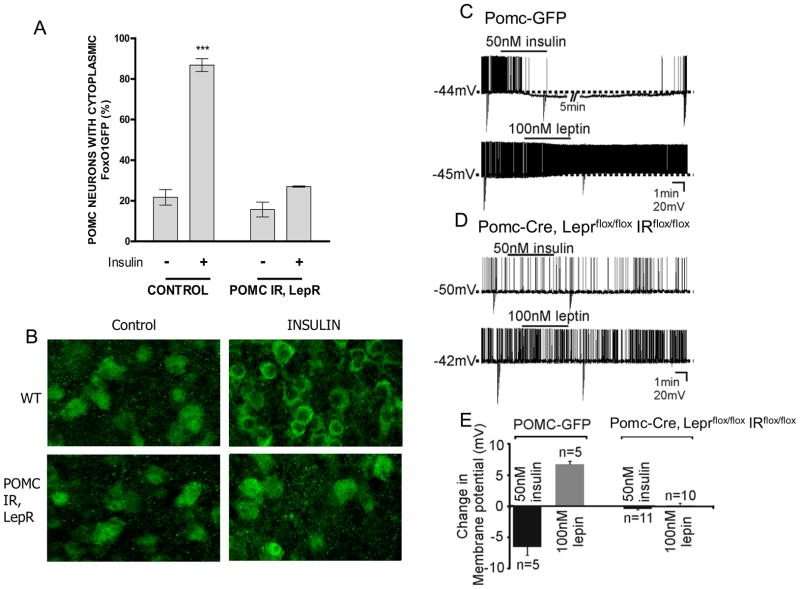
Figure 2. POMC neurons in Pomc-Cre, Leprflox/flox IRflox/flox mice do not respond to insulin.
A, Hypothalamic organotypic slices from FoxO1GFP-POMC reporter mice were treated with insulin (100 nM for 30 min) or vehicle and compared with slices from Pomc-Cre, Leprflox/flox IRflox/flox mice carrying the FoxO1GFP reporter and subjected to anti-GFP immunohistochemistry. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, The percentage of neurons with cytoplasmic FoxO1GFP. C. Current-clamp recordings at resting membrane potential depicting an insulin-induced hyperpolarization and a leptin-induced depolarization in separate POMC neurons from POMC-GFP mice. Downward deflections are responses to rectangular current steps. D. Current-clamp recordings show insulin and leptin fail to influence the membrane potential of POMC neurons in Pomc-Cre, Leprflox/flox IRflox/flox mice. E. Histogram of insulin- and leptin-induced responses in identified POMC neurons from POMC-GFP and Pomc-Cre, Leprflox/flox IRflox/flox mice. Values are means +/− SE. ***p < 0.001, compared by 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc. See also figure S2.