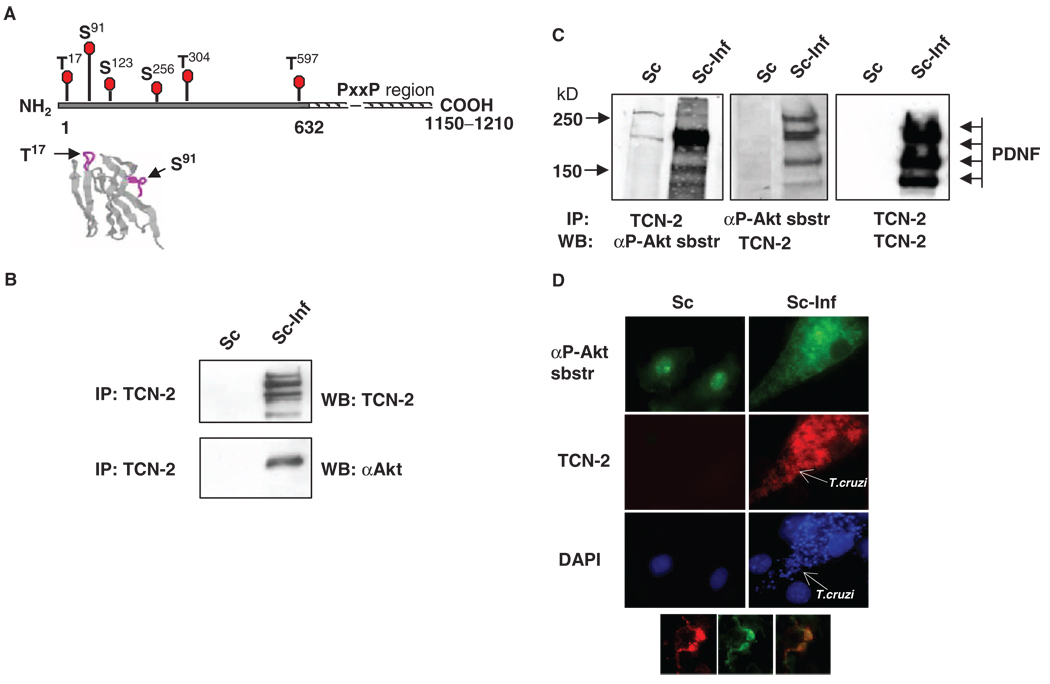
Fig. 1.
PDNF interacts with Akt and with an antibody against Akt-phosphorylated substrates in T. cruzi–infected Schwann cells. (A) Putative S and T within PDNF that are targets for phosphorylation by Akt. The N-terminal (solid line) and the C-terminal proline-rich region of tandem 12–amino acid residue repeats (hatched line) (19, 20). Below: Location of Thr17 and Ser91 in β-turns (purple lines) in the three-dimensional structure of PDNF (amino acid residues 1 to 124) (59). (B) PDNF coimmunoprecipitates with Akt. Lysates of uninfected (Sc) or T. cruzi–infected (Sc-Inf) Schwann cells (4 days PI) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with the PDNF-specific mAb TCN-2, followed by Western blotting analysis (WB) with TCN-2 or an antibody against Akt (αAkt). (C) PDNF coimmunoprecipitates with Akt-phosphorylated substrates. Lysates of Sc cells and Sc-Inf cells immunoprecipitated with TCN-2 were incubated with an antibody against Akt-phosphorylated substrates (left, αP-Akt sbstr) or with TCN-2 (right). The same lysates immunoprecipitated with an antibody against Akt-phosphorylated substrates were incubated with TCN-2 (middle). (D) PDNF colocalizes with an Akt-phosphorylated substrate in T. cruzi–infected Schwann cells. Uninfected and T. cruzi–infected Schwann cells were incubated with an antibody against Akt-phosphorylated substrates (green), the anti-PDNF mAb TCN-2 (red) and DAPI (blue). Inset shows two intracellular trypomastigotes that contain Akt-phosphorylated substrate (left) and PDNF (middle); (right) represents merged (left) and (middle). Original magnification, × 1000.