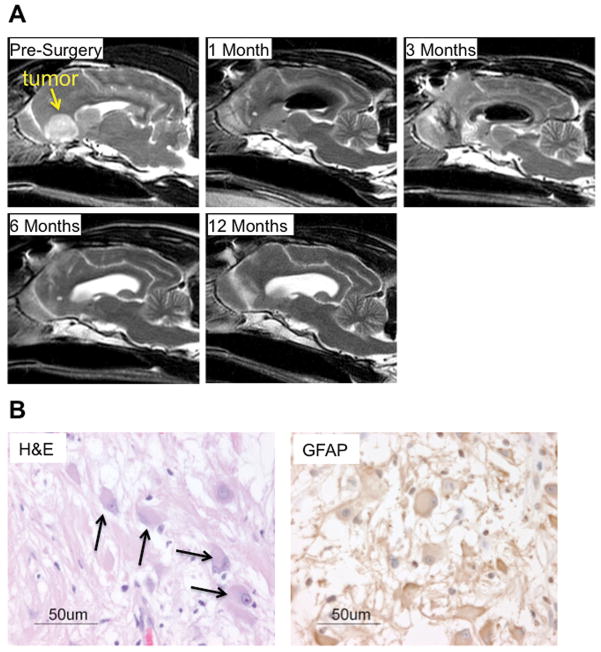
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging and histology of treated dog.
(a) T1-weighted sagittal images document nearly complete surgical resection of the bulk tumor mass (arrow). Ad-IFNγ was administered at the time of surgery by multiple bolus injections delivered into the brain parenchyma of cavity. Air was notable in the ventricle at 1 and 3 month scans. By seven months CSF replaced air in the ventricle and the resection cavity had closed. No tumor was apparent at one year. (b) Hematoxylin and eosin stain document presence of neoplastic gemistocytes within the tumor mass (arrows). Immunohistochemistry for GFAP confirms a glial origin of the tumor and supports the diagnoses of GemA.