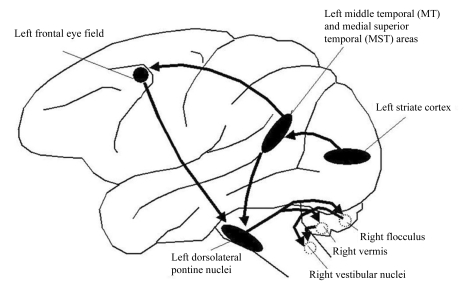
Figure 4.
A hypothetical scheme for horizontal smooth pursuit. Primary visual cortex (V1) projects to the homologue of the middle temporal visual area (MT) that in humans lies at the temporal-occipital-parietal junction. MT projects to the homologue of the medial superior temporal visual area (MST) and also to the frontal eye field (FEF). MST also receives inputs from its contralateral counterpart. MST projects through the retrolenticular portion of the internal capsule and the posterior portion of the cerebral peduncle to the dorsolateral pontine nucleus (DLPN). The DLPN also receives inputs important for pursuit from the FEF; these inputs descend in the medial portion of the cerebral peduncle. The DLPN projects, mainly contralaterally, to the flocculus, paraflocculus, and ventral uvula of the cerebellum; projections also pass to the dorsal vermis. The flocculus projects to the ipsilateral vestibular nuclei (VN), which in turn project to the contralateral abducens nucleus. Dotted circles show structures on the opposite side.