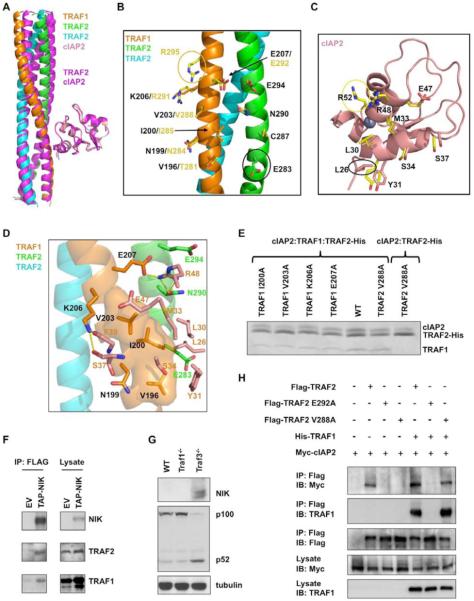
Figure 5.
The TRAF1: TRAF2: cIAP2 ternary complex
(A) Superposition of the cIAP2 molecule in the ternary complex structure with the cIAP2 molecule in the TRAF2: cIAP2 binary complex structure, showing the resulting orientational difference in the TRAF trimers. The TRAF2: cIAP2 complex is shown in magenta.
(B) A ribbon diagram of the TRAF1: TRAF2 heterotrimer shown with side chains involved in cIAP2 interaction. Side chains at the heterotrimer are shown with carbon atoms colored according to the ribbon colors. Equivalent side chains at the TRAF2 homotrimer are also shown, with carbon atoms in yellow. The yellow circle indicates the residue only involved in the TRAF2: cIAP2 interaction; the black circle indicates the residue only involved in the cIAP2 interaction in the heterotrimer.
(C) A ribbon diagram of the cIAP2 BIR1 domain, shown with side chains involved in the heterotrimer interaction. Side chains are shown with carbon atoms colored according to the ribbon colors. Equivalent side chains of cIAP2 involved in the TRAF2 homotrimer interaction are also shown, with carbon atoms in yellow. The yellow circle indicates the residue only involved in the TRAF2: cIAP2 interaction; the black circle indicates the residue only involved in the heterotrimer interaction.
(D) Detailed interaction between the TRAF1: TRAF2 heterotrimer and cIAP2. For clarity, only side chains of cIAP2 are shown.
(E) Mutational effects of the TRAF1: TRAF2 complex in cIAP2 interaction. The defective phenotype of the V288A mutation in TRAF2 can be rescued by WT TRAF1.
(F) Pulldown of TRAF1 and TRAF2 by NIK. NIK−/− MEFs were reconstituted with an empty vector (EV) or tandem affinity purification tag (TAP, with a CBP tag and a FLAG tag) fused NIK (TAP-NIK). The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag M2 beads followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
(G) Immunoassays on lysates from wild-type (WT), Traf1−/−, and Traf3−/− murine transformed B cells. Basal NIK level and p100 to p52 processing in whole cell extracts were detected by immunoblotting.
(H) Co-immunoprecipitation of lysates from HEK 293T cell co-expressing Myc-cIAP2 and Flag-TRAF2, Flag-TRAF2 E292A or Flag-TRAF2 V288A in the presence or absence of His-TRAF1. Lysates were incubated with anti-Flag M2 beads and TRAF2: cIAP2 and TRAF2: TRAF1 complexes were detected by immunoblot analysis against Myc and TRAF1 respectively. All experiments were done at least three times with similar results.