Figure 1.
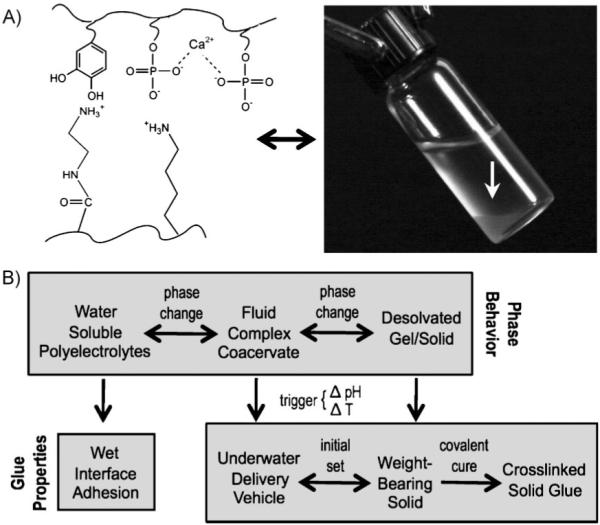
Complex coacervates as adhesives. A) The adhesive comprises dopamide containing poly-phosphate, poly-aminated gelatin, and divalent cations. Under the right conditions, the polyelectrolyte solution condenses into a complex coacervate phase (white arrow in photo). B) The top row represents the phase behavior of the polyelectrolytes. The bottom row connects the features of the phase behavior to solving the several problems of creating an underwater glue. The change from fluid complex coacervate to insoluble solid—the intial setting reation—is triggered by a change in the pH, temperature, or both. Irreversible covalent hardening occurs through oxidative coupling between catechol and primary amine sidechains.
