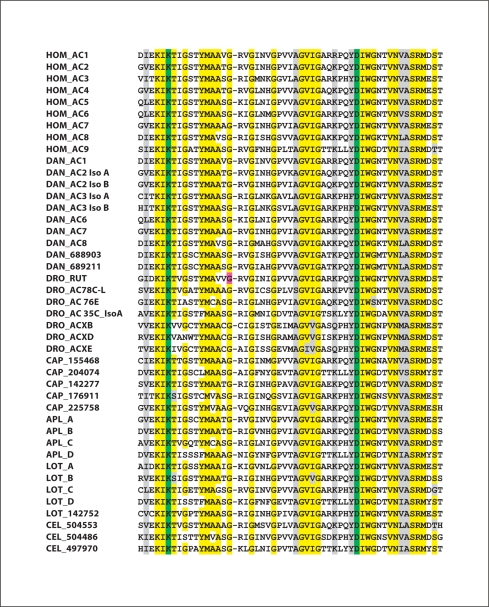
Fig. 3.
Results of a ClustalW analysis of highly conserved sequences within the catalytic domain of the C2A region of ACs. Residues highlighted in yellow represent amino acids conserved in 90% or more of the AC isoforms. Residues highlighted in grey represent conserved substitutions. Lysine and aspartate residues indicted in green distinguish adenylyl cyclases from guanylyl cyclases [Baker and Kelly, 2004]. The glycine residue in the Drosophila rutabaga AC highlighted in purple is Gly1026, which is altered to Arg in the rutabaga learning mutant, resulting in complete loss of catalytic activity [Levin et al., 1992]. For human (Hom), standard nomenclature is used; and for corresponding Danio (DAN) isoforms, the same nomenclature is employed. For Drosophila (DRO), gene names are used. For Aplysia (Apl) ACs, names are from NCBI and Lin et al. [in preparation]. For Lottia (Lot) isoforms that correspond to Aplysia isoforms, the same nomenclature is used. For C. elegans (Cel), protein IDs are from NCBI. For Capitella (Cap) and for one Lottia AC, names correspond to protein IDs from the JGI Genome site. For Drosophila, two of the members of the ACX family, ACXA and ACXC, have been omitted from the analysis, as they are extremely similar to ACXB. To facilitate comparison with the genome sites, AC IDs that are somewhat different from those in the databases are listed below. C. elegans: NP_504553; NP_504486, NP_497970. Danio AC1 = XP_685077; Danio AC2 iso A = XP_692173; Danio AC2 iso B = NP_001093457; Danio AC3 iso A = XP_700547; Danio AC3 iso B = XP_693142; Danio AC6 = XP_001922749; Danio AC7 = XP_001922494; Danio AC8 = NP_001137224; Drosophila ACXD = ACK77593; Lottia A = 141290; Lottia B = 187968/231713; Lottia C = 135065; Lottia D = 136240/170789. (For Lottia B and D, on JGI, the C1A and C2A domains were given two separate proteins numbers.)