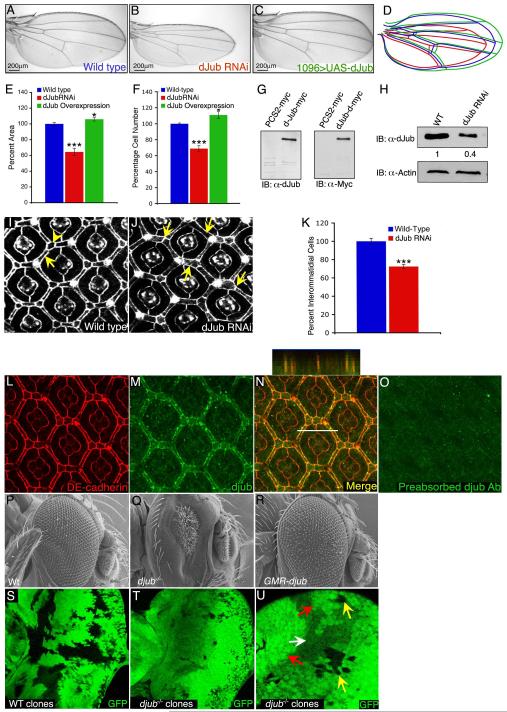
Figure 1. dJub regulates tissue size by controlling cell number.
(A-C) Wings from wt female flies (A), female flies expressing dJub RNAi (B), or female flies expressing dJub-mCherry transgene (C). 1096-Gal4 was used to drive RNAi or transgene expression. (D) Outlines of the wings in panels A-C. (E, F) Quantification of relative wing areas (E) and cell numbers (F) of genotypes in A-C. Area and cell number measurements were taken from the wing region located between veins L4 and L5, and wt defined as 100% (N=20 for each). (G) Extracts of mammalian HEK293 cells transfected with myc-dJub immunoblotted with dJub antiserum (left) or Myc antiserum (right). (H) Immunoblot analysis of dJub protein levels in wt or dJub RNAi-expressing larval eye imaginal discs. Actin serves as loading control. Relative amount of dJub protein is indicated below each lane. Mid-pupal wt eyes (I) or GMR-Gal4 driven dJub RNAi expressing eyes (J) stained for DE-cadherin. Secondary (arrows) and tertiary (arrowheads) interommatidial cells are highlighted. Loss of interommatidial cells in dJub RNAi expressing pupal eyes denoted by arrows (J). (K) Quantification of relative numbers of interommatidial cells in wt versus dJub RNAi pupal eye. Interommatidial cells were counted in 20 fields, each containing a cluster of at least 7 ommatidia. (L-O) Mid-pupal wt eyes stained for DE-cadherin (L), dJub (M), and merged image (N). Z-stack analysis of line in N is shown above panel N (N). (O) Immunostaining with dJub antiserum preabsorbed with immunizing peptide. (P-R) Scanning electron micrographs (SEMs) of female adult eyes. WT (Q), djubI generated via the EGUF-Hid method, which results in eyes composed almost entirely of mutant tissue (Q), and GMR-gal4 driven overexpression of UAS-dJub-mCherry transgene (R). (S-U) Female third-instar larval eye imaginal discs containing wt (S) or djubI mutant (T, U) clones marked by the absence of GFP expression (black). (U) Enlarged view of djubI and wt twin spot clones. Yellow arrow identifies djubI clones, red arrow identifies wt twin spot clone containing two copies of Ubi-GFP, and white arrow identifies tissue carrying one copy of Ubi-GFP. In all experiments wings and eyes were dissected from female flies. In graphs data are shown as mean percentages +/− standard deviation, with N= 20 for each genotype. (***) Represents p-value ≤ 0.001 and (*) represents p-value ≤ 0.05. Anterior is to the left for all larval imaginal discs.