Figure 5. Deletion of neuroD leads to increased NPY expression.
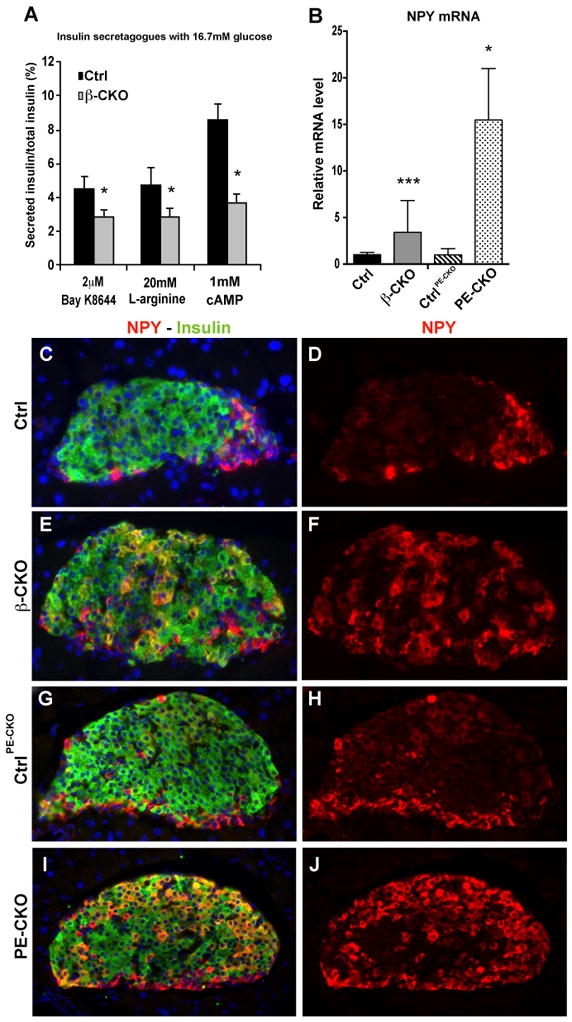
(A) Isolated islets from control and neuroD β-CKO mice treated with different insulin secretagogues (2uM BayK8644, 20mM L-arginine and 1mM dibutyryl cAMP) in the presence of 16.7mM glucose. Secreted insulin was normalized to total insulin in the islets (n= 6–9 per genotype). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of NPY mRNA in control, neuroD β-CKO and neuroD PE-CKO islets. The data were normalized to β-actin mRNA (n=4–8 per genotype) and presented as relative to the respective controls. (C–J) Coimmunostaining of neuropeptide Y (red) and insulin (green) in the pancreatic sections of control for neuroD β-CKO (C–D), neuroD β-CKO (E–F), control for neuroD PE-CKO (G–H) and neuroD PE-CKO (I–J). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Original magnification was 200x. * P≤0.05, ** P≤0.01 and *** P≤0.001.
