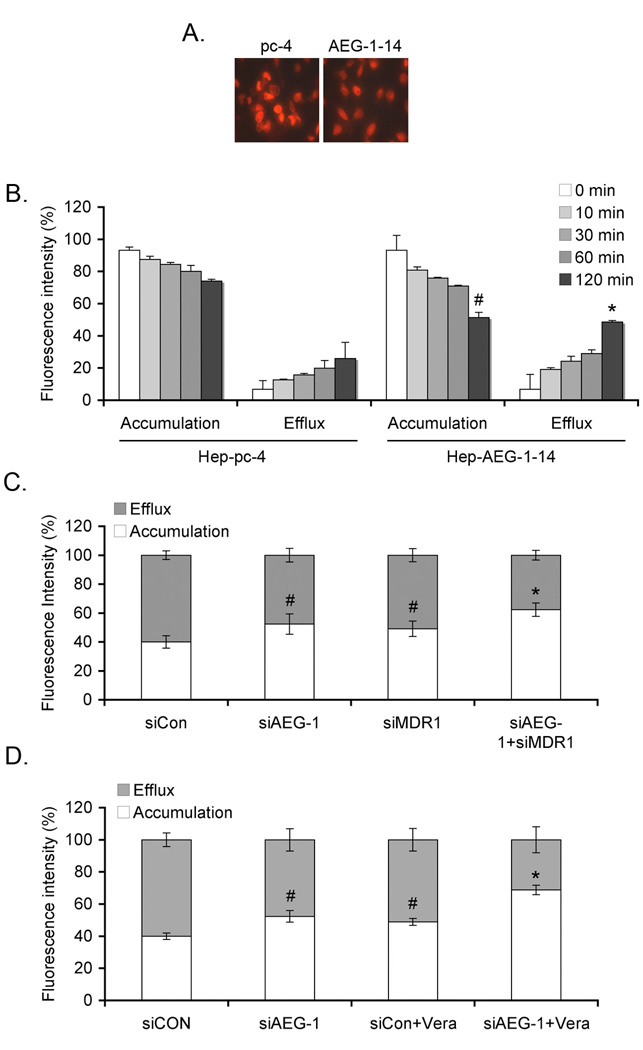
Fig. 3.
AEG-1 increases DOX efflux and decreases DOX accumulation. A. Hep-pc-4 and Hep-AEG-1-14 cells were treated with 3.44 µM Dox for 2 h, washed in PBS several times and incubated with DOX-free complete growth media for 2 h. Intracellular accumulation of DOX was determined by fluoroscence microscopy. B. Cells were treated as in A for the indicated time points. Cell pellets were analyzed for intracellular DOX accumulation and the bathing media were used for efflux assay as described in Materials and Methods. #: p<0.01 vs accumulation in Hep-pc-4 cells at 120 min; *: p<0.01 vs efflux in Hep-pc-4 cells at 120 min. C. Hep-AEG-1-14 cells were transfected with siCon, siAEG-1 or siMDR1 or a combination of siAEG-1 and siMDR1 and treated with 3.44 µM Dox for 2 h. DOX accumulation and efflux assays were performed as in B. #: p<0.05 vs siCon; *: p<0.01 vs siCon. D. Hep-AEG-1-14 cells were transfected with siCon or siAEG-1, treated with Verapamil (Vera; 10 µM) and treated with 3.44 µM Dox for 2 h. DOX accumulation and efflux assays were performed as in B. #: p<0.05 vs siCon; *: p<0.01 vs siCon. Data represents mean ± SEM.