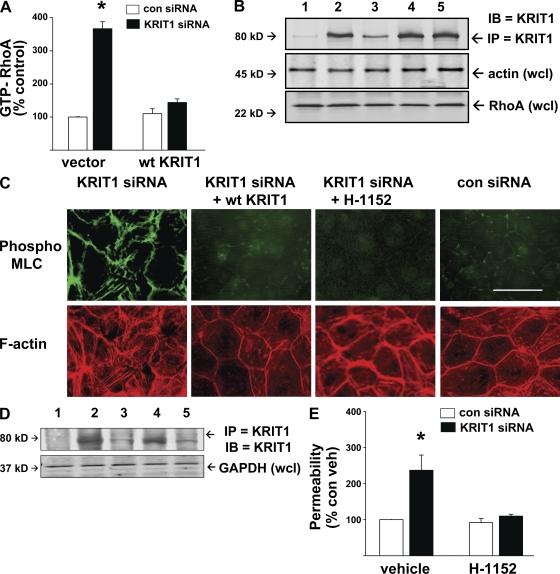
Figure 1.
KRIT1 inhibits RhoA and its effector ROCK to reduce MLC phosphorylation and permeability in vitro. (A) HUVECs treated with control or KRIT1 siRNA were evaluated for RhoA activity. KRIT1-depleted cells had a 3.5-fold increase in GTP-RhoA compared with control, reversible by cotransfection with WT KRIT1 bearing a knockdown-resistant silent mutation. Error bars are means and SE of n = 6. *, P < 0.001 compared with vector-only control siRNA. (B) Total RhoA is shown by immunoblotting, and equal protein content per sample is shown by actin loading. KRIT1 siRNA efficacy is shown by immunoprecipitated KRIT1 content. 1, control IP with mouse IgG; 2, control siRNA; 3, KRIT1 siRNA; 4, control siRNA + KRIT1 complementary DNA (cDNA); 5, KRIT1 siRNA + KRIT1 cDNA. (C) KRIT1 depletion increased MLC phosphorylation and f-actin stress fiber content. Reconstitution with WT KRIT1 prevented pMLC increase and reduced stress fibers. Treatment of KRIT1-depleted cells with ROCK inhibitor H-1152 also prevented MLC phosphorylation and stress fiber formation, indicating that ROCK acts downstream of KRIT1. Bar, 50 µm. (D) siRNA efficacy is shown by Western blot probed for KRIT1. 1, control IgG IP; 2, control siRNA; 3, KRIT1 siRNA; 4, KRIT1 siRNA+ KRIT1 cDNA; 5, KRIT1 siRNA + H-1152. (E) KRIT1 depletion increases HUVEC monolayer permeability in Transwell assays. The increase is reversible by H-1152 treatment, indicating that KRIT1 functions to inhibit ROCK-mediated monolayer leak. Error bars are means ± SE of n = 6. *, P < 0.001 compared with control siRNA