Figure 3.
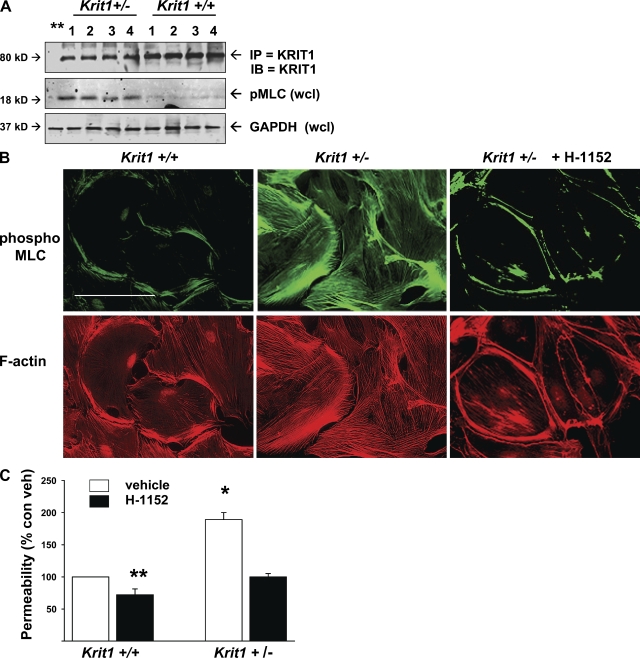
Krit1+/− mouse endothelial cells have increased in vivo and in vitro pMLC and in vitro leak. (A) Endothelial cells were isolated from Krit1+/+ and Krit1+/− mouse brain, lung, liver, and kidney as described in Materials and methods, lysed, and Western blotted for immunoprecipitated KRIT1 protein and for pMLC in whole cell lysate. 1, brain; 2, lung; 3, liver; 4, kidney. Endothelial cells from Krit1+/− mice had similar KRIT1 protein expression in all organs but ∼1/2 the amount seen in Krit1+/+ mice. Endothelial cells from all organs in Krit1+/− mice exhibited increased pMLC content in vitro. (B) Isolated pulmonary endothelial cells grown on FN-coated coverslips were also stained for pMLC and f-actin content. Krit1+/− cells exhibited an increase in both. Bar, 50 µm. (C) In vitro permeability assay of isolated pulmonary endothelial cells. Krit1+/− endothelial monolayers were twofold more permeable than WT. Permeability was reduced by the ROCK inhibitor H-1152. Error bars are means ± SE (n = 6). *, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated Krit1+/+.