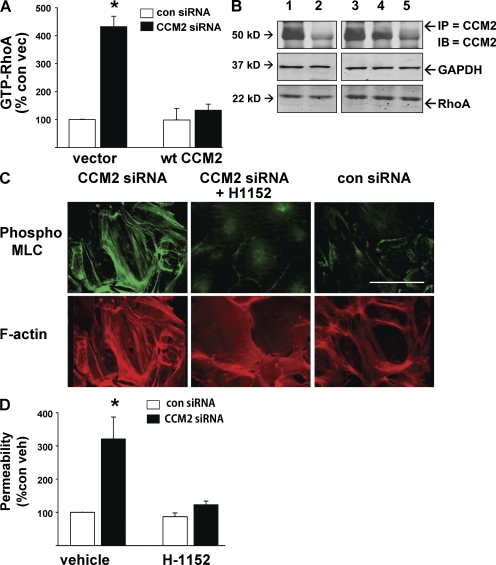
Figure 5.
CCM2 depletion increases RhoA and ROCK activity in vitro. (A) HUVECs were treated with CCM2 or control siRNA, with or without WT CCM2 bearing a silent mutation resistant to knockdown. Depletion of CCM2 produced a four- to sixfold increase in GTP-RhoA, reversible by cotransfection with WT CCM2. Error bars are means ± SE (n = 6). *, P < 0.001 compared with control siRNA. (B) Total RhoA is equal in all treatments. Equal sample protein is shown by GAPDH. CCM2 knockdown and reconstitution efficacy are shown by immunoprecipitated CCM2. 1, vector + control siRNA; 2, vector + CCM2 siRNA; 3, control siRNA + WT CCM2 cDNA; 4, CCM2 siRNA + WT CCM2 cDNA; 5, control rabbit IgG IP. (C) CCM2 depletion by siRNA increases pMLC and stress fiber content of HUVEC, reversible by treatment with ROCK inhibitor H-1152. Bar, 50 µm. (D) As previously seen with KRIT1, CCM2 presence is required for suppression of ROCK-mediated monolayer permeability. Error bars are means ± SE (n = 4). *, P < 0.001 compared with vehicle-treated control siRNA.