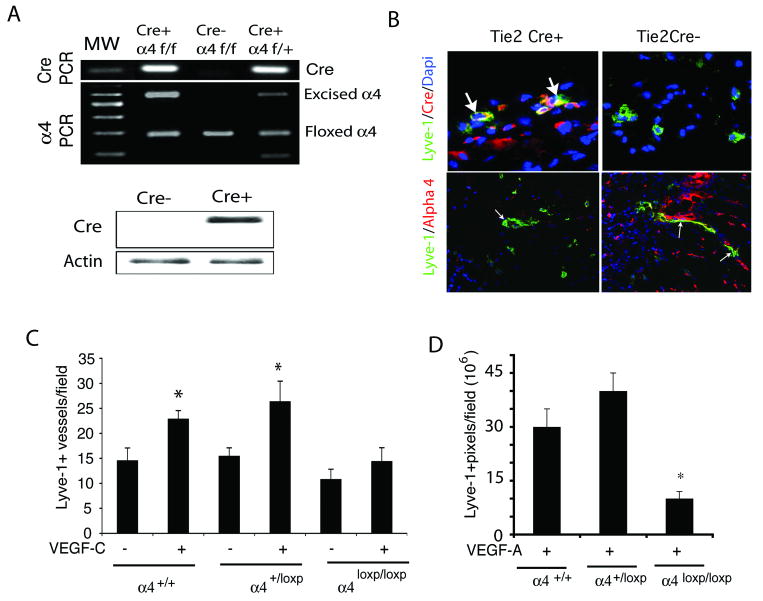
Figure 3. Inhibition of VEGF-C lymphangiogenesis in integrin α4 mutant animals.
(A) Upper, Genomic PCR analysis of Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/loxp, Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/+ and Tie2Cre(-) α4loxp/loxp mice for Cre-recombinase (100bp), intact integrin α4 (180bp), floxed α4 (280bp) and excised α4 (600bp). Lower, Western blotting of Cre-recombinase (38 kD) and beta-actin (42kD) in lung lysates from Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/loxp and Tie2Cre(-) α4loxp/loxp mice. (B) Upper, Cryosections of VEGF-C saturated Matrigel plugs in Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/loxp and Tie2Cre (-) α4loxp/loxp mice immunostained to detect Cre (red) and Lyve-1+ expression (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Cre+ vessels are indicated by arrows. Lower, Cryosections of VEGF-C saturated Matrigel plugs in Tie2Cre(+) and Tie2Cre (-) mice immunostained to detect integrin α4 (red) and Lyve-1 (green) positive vessels (arrows). (C-D) Mean Lyve1+ lymphatic vessels/field +/- SEM in Matrigel plugs from (C) VEGF-C or (D) VEGF-A stimulated Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/loxp, Tie2Cre(+)α4loxp/+ and Tie2Cre(-) α4loxp/loxp mice (*p<0.007).