Figure 1.
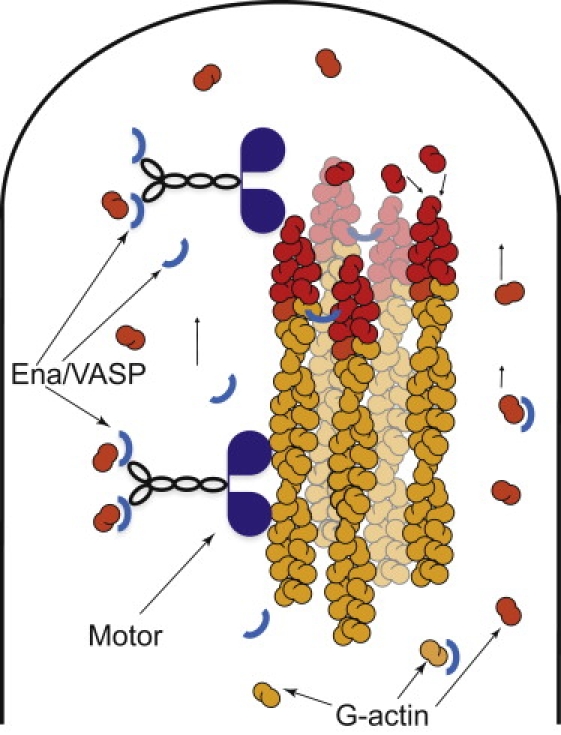
A schematic representation of the filopodial tip in the model is shown. A bundle of polymerizing actin filaments is enveloped by membrane which affects polymerization rates. Transported G-actin must dissociate before polymerization. Retrograde flow pulls filaments back with constant velocity. Myosin X motors travel the filaments in a directed fashion toward the barbed ends at the filopodial tip. Ena/VASP serves as a scaffold between G-actin monomers and motor molecules, and it is consumed near the tip due to cross-linking of the filaments.
