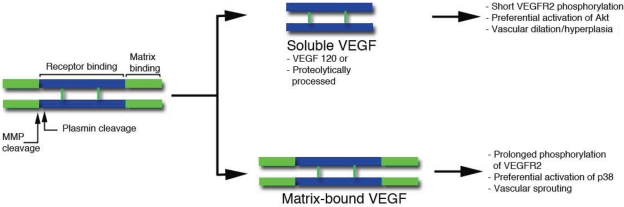
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of VEGF. Two monomers are held together in an anti-parallel orientation by disulfide bonds. The central region (blue) is the receptor binding domain, which binds both VEGFR1 and 2, and is encoded by exons 2–5. The C-terminal region (green) includes the matrix-binding motif (encoded by a variable number and combination of exons 6a, 6b, and 7). Amino acids encoded by exon 8 are present in all VEGF forms. Plasmin and some matrix metalloproteases can sever (by proteolysis) the receptor-binding motif from the extracellular matrix binding domain. Soluble VEGF lacks the matrix-binding region either because it is secreted as a short alternative spliced form (VEGF120) or because is modified post-translationally by plasmin or MMPs. The effects of soluble and bound forms are indicated on the right and based on our previous data.67,69