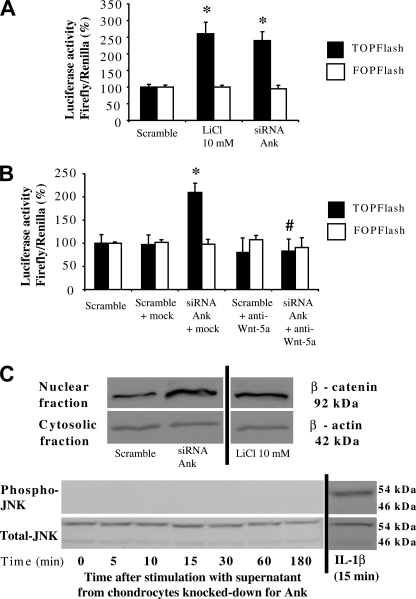
FIGURE 4.
Influence of transitory knock-down of Ank on the canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways activation. A, effect of conditioned supernatant on Tcf/Lef pathway activation. Chondrocytes were electroporated either with active (TOPFlash) or with inactive (FOPFlash) Tcf/Lef reporter genes, and with CMV-Renilla reporter gene before stimulation with supernatant from cells transfected with Ank siRNA for 48 h. Cells were stimulated with LiCl (10 mm) as a positive control. Results are presented in histograms as mean luciferase activity ratio of firefly/Renilla (± S.D.) (n = 4). B, effect of neutralized supernatant on Tcf/Lef pathway activation. Conditioned supernatants were neutralized or not for 1 h at 37 °C, using either mock (anti-β-actin) or anti-Wnt-5a antibodies. Chondrocytes transfected with reporter genes were stimulated with these supernatants for 48 h. Results are presented in histograms as mean luciferase activity ratio of firefly/Renilla (± S.D.) (n = 4). Statistically significant differences from Scramble are indicated as *, p < 0.05, and from mock as #, p < 0.05. C, effect of conditioned supernatants on the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and on the activation of the non-canonical Wnt pathways. Chondrocytes were stimulated with supernatants from cells transfected with either scramble or Ank siRNA for 48 h or the indicated times. Cells stimulated with 10 mm LiCl were used as a positive control for nuclear translocation of β-catenin, and cells stimulated with 10 ng/ml of IL-1β for 15 min were used as a positive control for JNK activation. Proteins were extracted and subjected to Western blotting using either anti-β-catenin, or anti-phospho- and anti-total-JNK antibodies. The relative abundance of β-catenin was normalized to that of β-actin protein. Images presented are representative of three independent experiments.