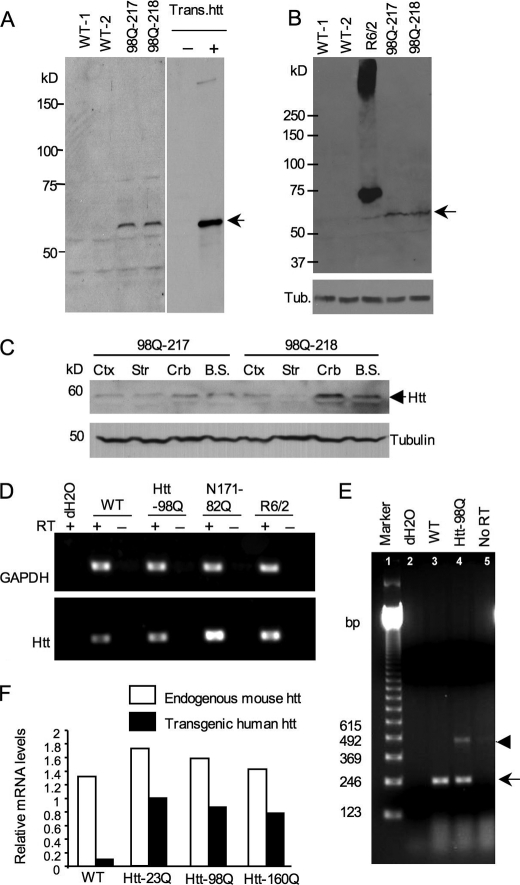
FIGURE 2.
Expression levels of transgenic htt in htt-98Q transgenic mice. A, Western blot analysis of the expression of transgenic htt (N-terminal htt (208 amino acids) containing 98Q) in whole brain lysates using anti-htt antibody (EM48). Mouse brain extracts of htt-98Q mice were obtained from two independent transgenic mouse lines (98Q-217 and 98Q-218 lines). Transfected htt in HEK293 cells served as a control (arrow). B, Western blots with EM48 reveals the low level of transgenic htt-98Q compared with transgenic htt in R6/2 mouse brain. The arrow indicates htt-98Q. C, EM48 Western blotting of different brain regional tissues of htt-98Q transgenic mice. D, RT-PCR analysis of the transcript levels of transgenic htt in WT and HD (htt-98Q, N171–82Q, and R6/2) mouse brain cortex tissues. Primers that can amplify both mouse and transgenic htt were used for PCR. GAPDH was also amplified and served as an internal control. RT, reverse transcriptase. E, RT-PCR analysis of cultured astrocytes showing lower levels of transgenic htt-98Q (arrowhead) than endogenous mouse htt (arrow). Primers that amplify the CAG repeat were used in RT-PCR. F, real-time PCR of cultured astrocytes from wild type and transgenic mice (htt-23Q, htt-98Q, htt-160Q) that express mutant htt in astrocytes. The relative expression levels of transgenic htt were normalized to endogenous GAPDH levels and were obtained from three independent real-time PCR assays.