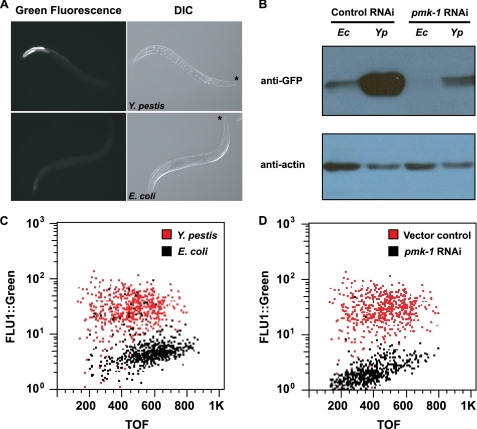
FIGURE 3.
PMK-1 MAPK contributes to the induction of C. elegans genes in response to Y. pestis. A, AY101 acIs101[pDB09.1(pF35E12.5:: gfp);pRF4(rol-6(su1006))] animals containing a transcriptional reporter for F35E12.5 were exposed to Y. pestis (top panels) or E. coli (bottom panels) for 24 h and imaged using fluorescence microscopy. An asterisk indicates the head of the animals. DIC, differential interference contrast. B, Western blot analysis of GFP expression levels in AY101 animals. AY101 transgenic animals were treated with a control vector or pmk-1-specific RNAi. Total nematode lysates were collected from 50 adult animals following 24 h of exposure to E. coli (Ec) or Y. pestis (Yp). C and D, analysis of GFP fluorescence intensity in AY101 animals using the COPAS BIOSORT instrument (Union Biometrica, Holliston, MA) (45). C, AY101 animals treated with a control RNAi vector were exposed to Y. pestis or E. coli for 24 h. D, AY101 animals treated with control vector or pmk-1 RNAi were exposed to Y. pestis. GFP fluorescence intensity (FLU-1) was plotted against adult animal size, measured as time of flight (TOF). Each dot represents an individual nematode. All results are representative of three or more independent experiments.