Figure 1.
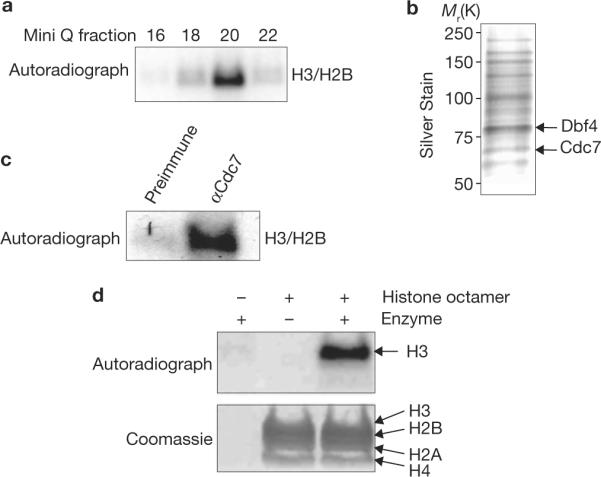
Identification of the Cdc7–Dbf4 histone kinase complex. (a) Histone kinase assays using purified chromatographic fractions from yeast whole-cell extracts. Fractions from the final Mini Q column are shown. (b) Silver stain of Mini Q fraction 20, the peak of histone kinase activity from a. Proteins identified by mass spectrometry and/or confirmed by western blot are labelled; unlabelled bands await confirmation. (c) Histone kinase assays using proteins immunoprecipitated by either anti-Cdc7 antibody or pre-immune sera from extracts that were bound to and eluted from Ni2+-NTA agarose resin. (d) Kinase assays using histone octamers and the purified native Cdc7–TAP complex as indicated.
