Fig. 7.
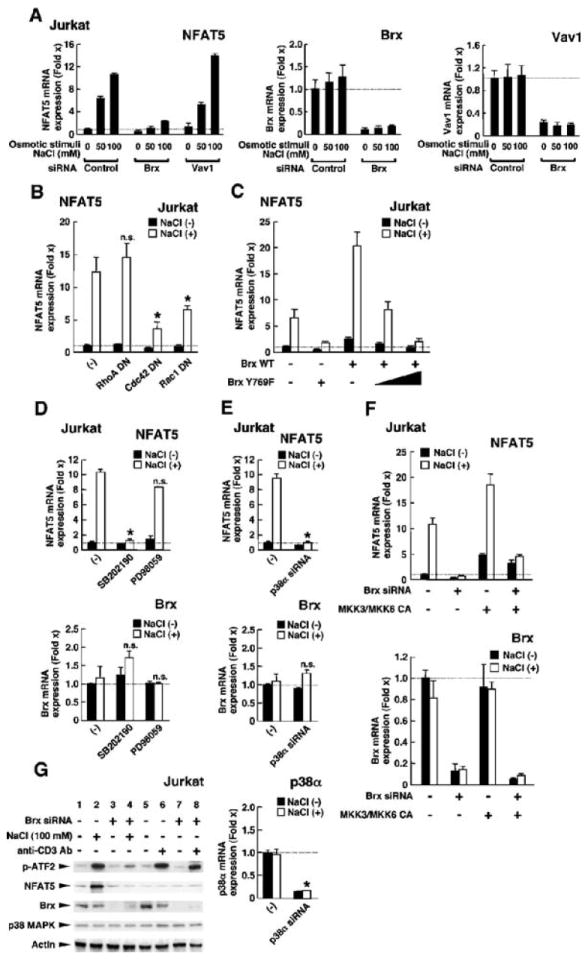
The GEF domain of Brx, as well as Cdc42, Rac1, and p38 MAPK, are all required for an osmotic stimulus to induce the expression of nfat5 mRNA. (A) Brx, but not Vav1, is necessary for the induction of nfat5 expression in Jurkat cells in response to osmotic stimuli. Jurkat cells were transfected with control, Brx-specific siRNA, or Vav1-specific siRNA and incubated with the indicated concentrations of NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative abundance of nfat5 (left), brx (middle), and vav1 (right) mRNAs compared with baseline (the value obtained from the cells transfected with control siRNA and incubated in the absence of NaCl). (B) DN mutants of Cdc42 and Rac1, but not RhoA, suppress induction of nfat5 expression in Jurkat cells in response to osmotic stimuli. Jurkat cells were transfected with plasmids expressing DN mutants of RhoA, Cdc42, or Rac1 (RhoAT19N, Cdc42T17N, and Rac1T17N, respectively) and incubated with 100 mM NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative abundance of nfat5 mRNA compared with baseline (the value obtained from cells transfected with control plasmid and incubated in the absence of NaCl). *P < 0.01; n.s., not significant (the experiment was peformed in triplicate). (C) Induction of the expression of nfat5 mRNA in Jurkat cells in response to an osmotic stimulus requires the GEF domain of Brx, whereas a GEF-defective mutant Brx acts in a DN manner. Jurkat cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding WT Brx or the GEF-inactive mutant Brx and incubated with 100 mM NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative abundance of nfat5 mRNA compared with baseline (the value obtained from cells transfected with control plasmid and incubated in the absence of NaCl). (D) p38 MAPK, but not ERK1/2, is necessary for an osmotic stimulus to induce the expression of nfat5 mRNA in Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were incubated with 2 μM of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190 or 10 μM of the MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 in the absence or presence of 100 mM NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative abundance of nfat5 (top) and brx (bottom) mRNAs compared with baseline. *P < 0.01; n.s.: not significant (the experiment was performed in triplicate). (E) siRNA against p38α abolishes osmotic stimulus–induced expression of nfat5 mRNA. Jurkat cells were transfected with control or p38α-specific siRNA and cultured in the absence or presence of 100 mM NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative abundance of nfat5 (top), brx (center), and p38α (bottom) mRNAs compared with baseline (cells transfected with control siRNA and cultured in the absence of NaCl). *P < 0.01; n.s., not significant (the experiment was performed in triplicate). (F) Expression of the CA forms of MKK3 and MKK6 rescues the attenuation of osmotic stimulus–induced nfat5 expression caused by siRNA-mediated knockdown of Brx. Jurkat cells were transfected with control or Brx-specific siRNA in the absence or presence of MKK3- or MKK6-expressing plasmids and were cultured with or without 100 mM NaCl. Data shown represent the mean fold difference ± SEM in the relative expression of nfat5 (top) and brx (bottom) mRNAs compared with baseline (cells transfected with control siRNA and cultured in the absence of NaCl). (G) Osmotic stimulus activates p38 MAPK through Brx in Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were transfected with control or Brx-specific siRNA and cultured in the absence or presence of 100 mM NaCl or 10 μg/ml of anti-CD3. The kinase activity of p38 MAPK was evaluated by examining the abundance of phosphorylated ATF2 by Western blotting (top gel). The abundances of NFAT5, Brx, and p38 MAPK proteins were also examined (second to fourth gels) by Western blotting. Actin (bottom gel) was used as a loading control.
