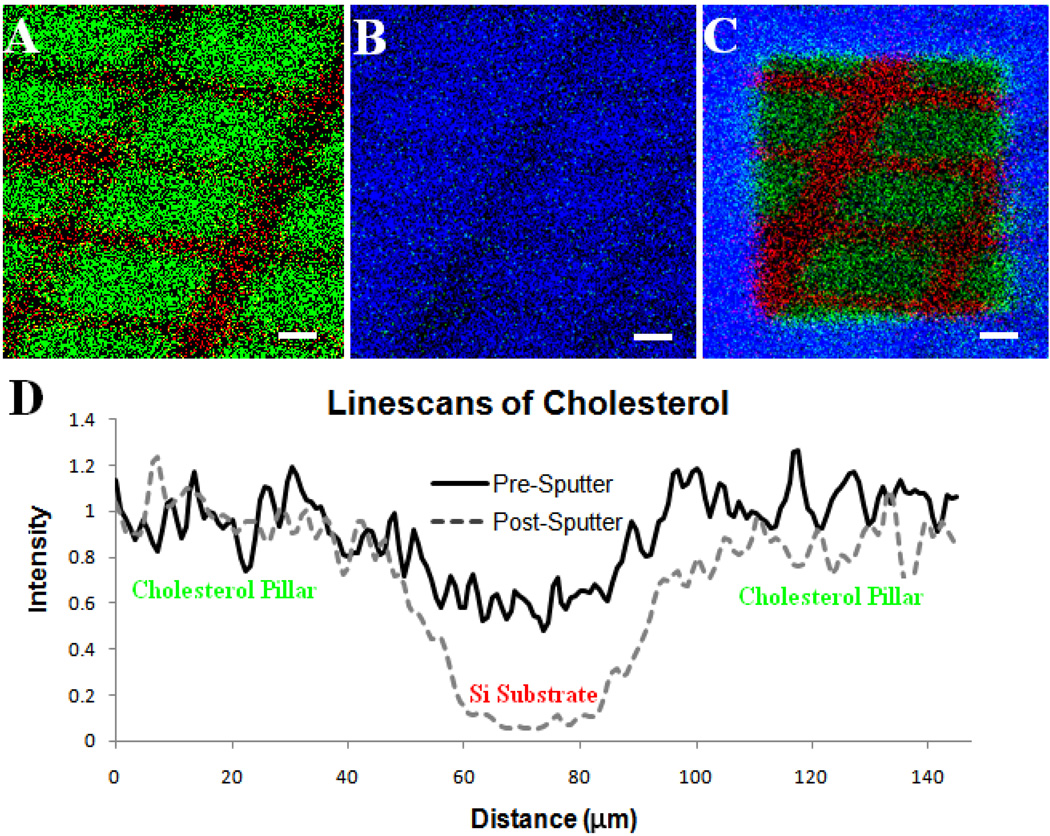
Figure 1.
(A.) Positive SIMS image of patterned cholesterol film on silicon created using physical vapor deposition, m/z 369 shown in green and m/z 28 in red. (B) The film was then cooled in vacuum (−196°C) and water was allowed to deposit, m/z 18 shown in blue and m/z 369 in green. The cholesterol layer is almost completely covered in water. (C.) After etching with a dose of 1013 C60+ ions/cm2 the patterned film beneath is revealed with maintained spatial integrity. (D.) Line scans across the film features reveal that the distribution of cholesterol on the surface is maintained when C60+ is used to remove the water overlayer versus when the surface is not cleaned with the C60+ nanotome. Scale bars are 25 µm.