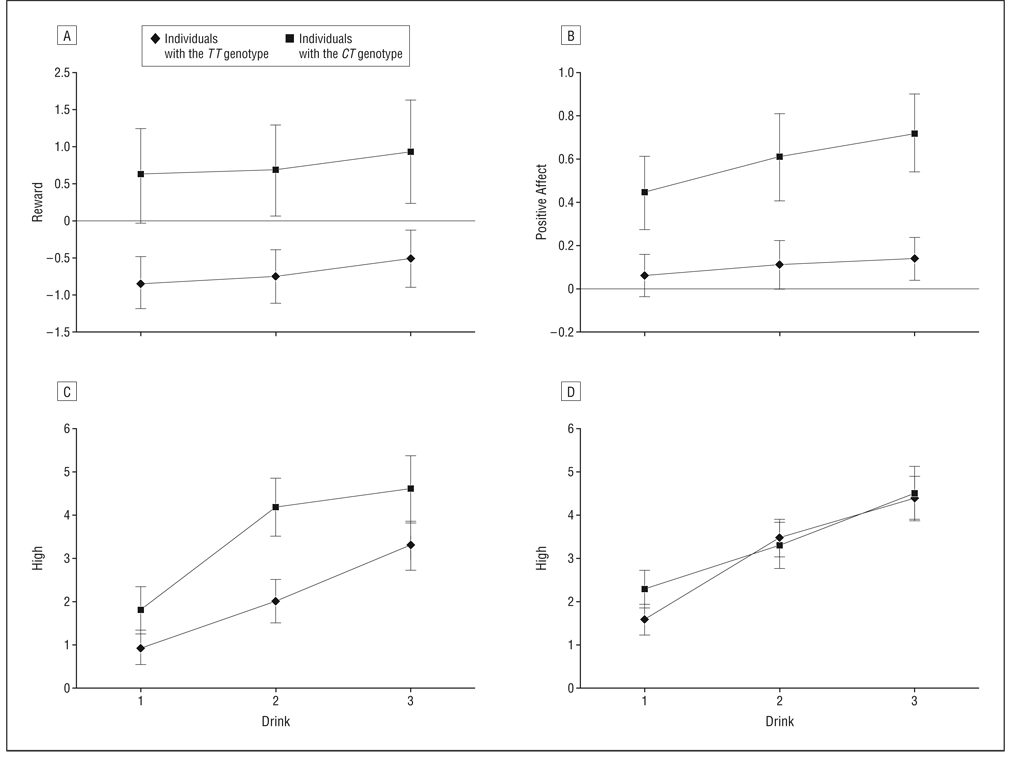
Figure 4.
Short-term effects of alcohol on subjective reward for each genotype group. Individuals with the CT genotype demonstrated significantly greater mean subjective reward (A) and positive affect (B) after alcohol consumption. In a replication and extension of this work, genotype was a significant moderator of the effect of medication on subjective high such that individuals with the CT genotype reported subjective high in the cyproheptadine hydrochloride (control) condition (C) but not in the olanzapine condition (D). Error bars represent SE.