FIGURE 1.
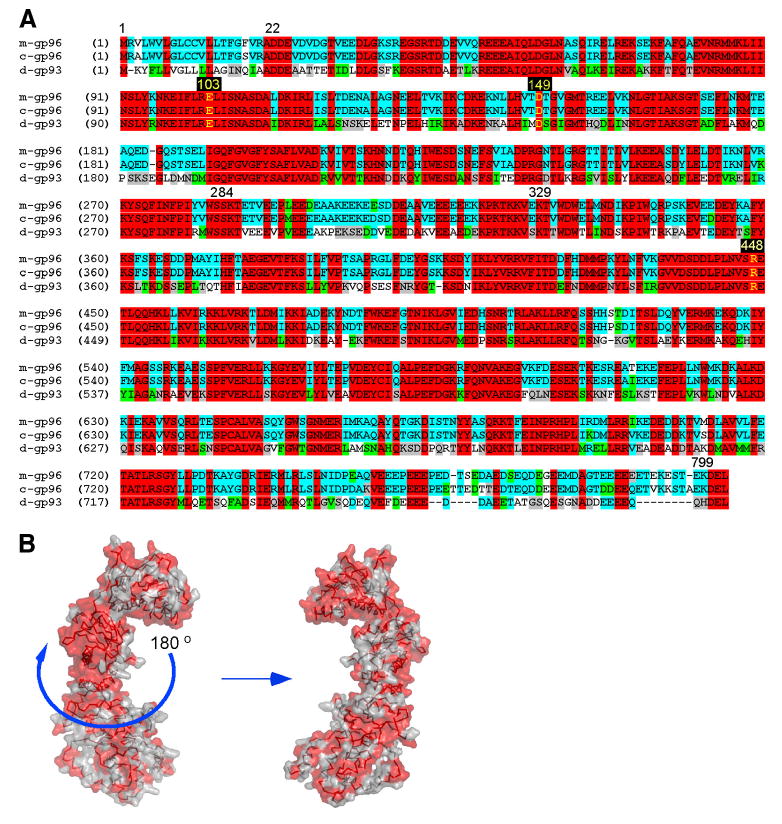
Sequence and structural conservation between Drosophila gp93 and the mammalian gp96. A, Sequence alignment of mouse gp96 (m-gp96), canine gp96 (c-gp96), and Drosophila gp93 (d-gp93) with amino acids corresponding to the ends of domains written numerically, and key residues involved in ATP binding and hydrolysis highlighted in yellow. Red, identical among all three; blue, conserved between two; green, similar class of amino acid; gray, weakly similar; white, nonconserved. B, Molecular surface representation of the canine gp96 monomer with N terminus pointing upward. Red solvent-accessible surfaces identify invariant residues between gp93 and gp96.
