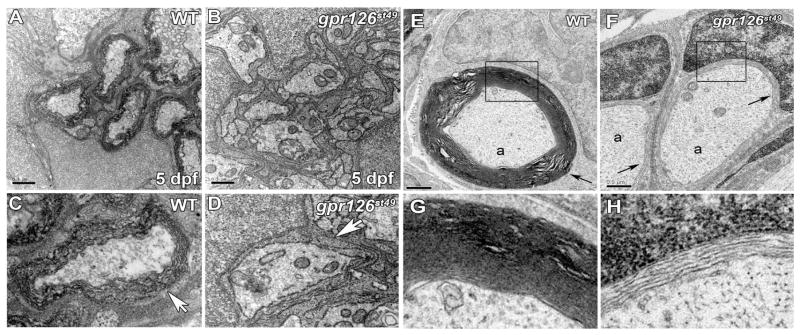
Fig. 3.
Schwann cells sort, but do not myelinate axons in gpr126st49 mutants. (A) Transmission electron micrograph showing cross-section through a WT PLLn at 5 dpf. (B) Transmission electron micrograph showing cross-section through a gpr126st49 mutant PLLn at 5 dpf. (C) Magnified view of a WT axon wrapped by several layers of myelin (arrow). (D) Magnified view of a gpr126st49 mutant axon showing that Schwann cell cytoplasm surrounds the axon (arrow), but does not turn more than 1.5 times around the axon. For (A, B), scale bar = 0.5 μm. (E) Transmission electron micrograph showing cross-section through a WT PLLn at 6 months of age. An axon (a) surrounded by compact myelin (arrow) is shown. (F) Transmission electron micrograph showing cross-section through a gpr126st49 mutant PLLn at 6 months of age. Axons (a) surrounded by a few loose wraps of Schwann cell cytoplasm (arrow) are shown. For (E) and (F), scale bar = 0.5 μm. (G) Magnified view of boxed region in (E) showing compact myelin surrounding an axon in WT PLLn. (H) Magnified view of boxed region in (F) showing loose Schwann cell cytoplasm surrounding an axon in gpr126st49 mutant PLLn. See Fig. S10 for quantification of these experiments.