Fig. 1.
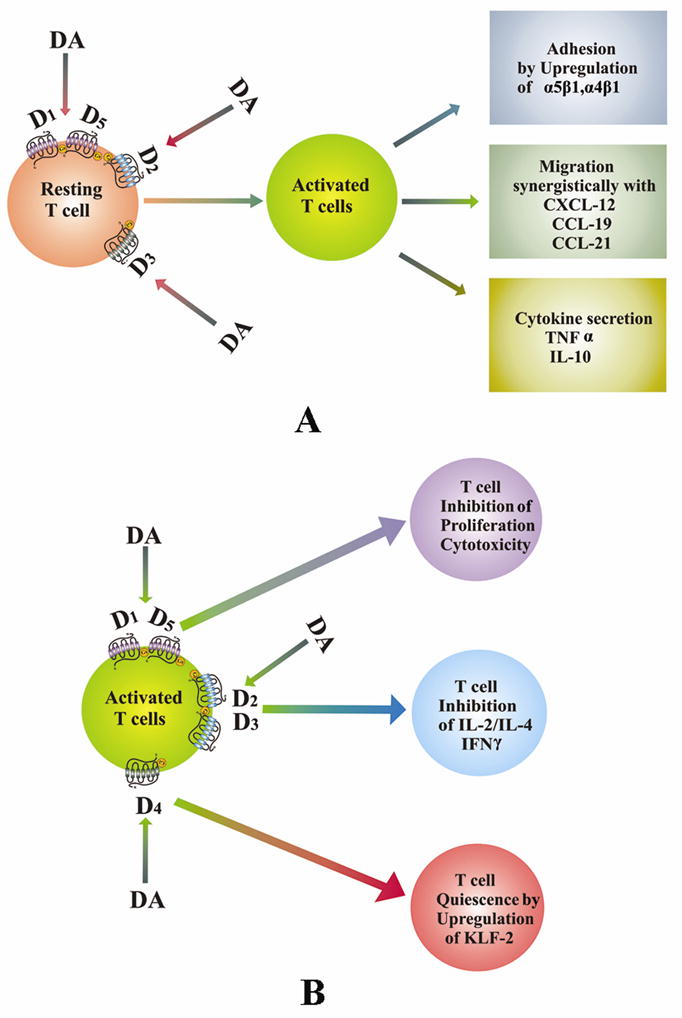
Role of dopamine in T cell functions. (A). DA activates naïve or resting T cells. DA by acting through its receptors stimulates adhesion, migration and cytokine secretion by these cells. (B). DA inhibits activated T cells. DA inhibits the activation of T cells when present during stimulation of T cell receptors and thus inhibits proliferation, cytokine secretion and induces T cell quiescence in these cells by acting through DA receptors. DA, dopamine; D1–D5, dopamine D1–D5 receptors.
