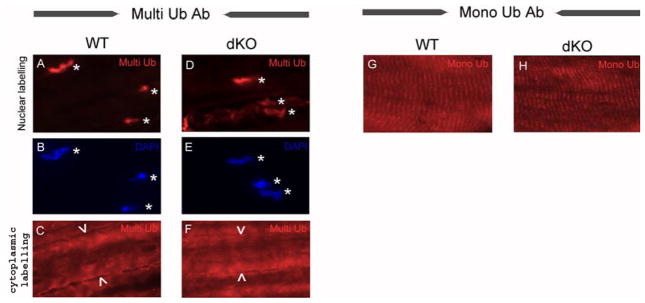
Figure 6. Ubiquitin immunolocalization in skeletal muscle fiber.
Immunofluorescence of longitudinal sections of tibialis anterior muscle using a multi-ubiquitin (A, C, D, F) and a mono-ubiquitin specific antibody (G, H); ubiquitin epitopes were detected in red. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI in blue (see B and E). Multi-ubiquitin and DAPI labelings co-localized both in wild type (WT, A and B) and in MuRF1/MuRF2 double knockout tibialis anterior muscles (dKO, D and E); for co-localization see asterisks in A and D. In addition, the multi-ubiquitin antibody labeled the cytoplasm diffusely, both in WT (C) and dKO (F; arrow heads indicate the limits of one skeletal muscle fiber). The mono-ubiquitin specific antibody detected a striated pattern, both in WT (G) and dKO (H) animals. No differences were noted in ubiquitin distribution between WT and dKO samples (multi-ubiquitin: compare A and D, C and F; mono-ubiquitin: compare G and H).