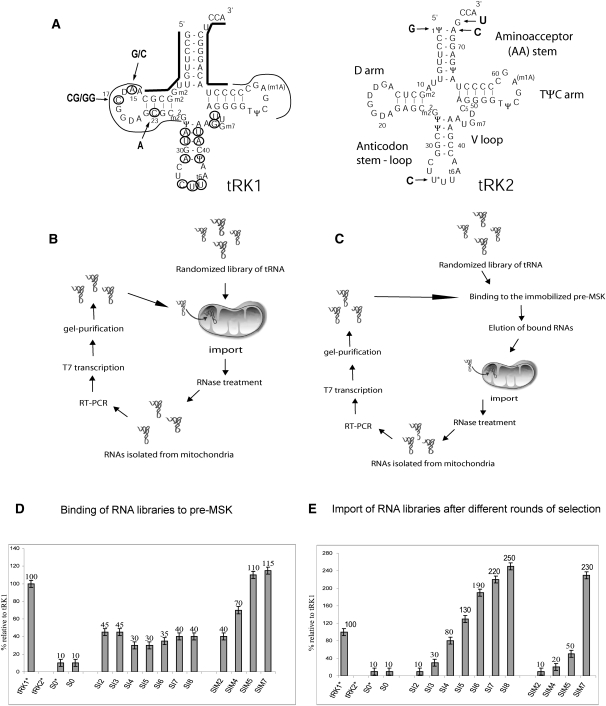
FIGURE 1.
(A) Cloverleaf structures of yeast lysine tRNAs, partially imported into mitochondria tRK1 and nonimported tRK2. The import determinants identified previously are indicated by arrows on the tRK2 structure. The tRK1 regions determined by oligonucleotides used for RT-PCR are shown by bold lines, residues that have been randomized for SELEX experiment are circled, and regions conserved in all the selected RNA aptamers are indicated by thin lines. Selected substitutions in the D-arm of tRK1 are shown by arrows. (B,C) Strategy for in organello RNA selection. Scheme of randomized RNA library selection (B) for import into isolated yeast mitochondria and (C) for both affinity to preMSK1p and mitochondrial import. (D,E) Characterization of RNA pools resulting from different rounds of selection: (D) preMSK1p-binding capacity; (E) efficiency of mitochondrial import, in percent relative to tRK1. (S0) Initial RNA library; (SI2–SI8) RNA pools after two to eight rounds of selection for the import into mitochondria; (SIM2–SIM7) RNA pools after two to seven rounds of selection for preMSK1p binding and mitochondrial import. RNAs marked by * were aminoacylated prior to the test. All experiments were performed at least twice in an independent way; standard deviations values are indicated.