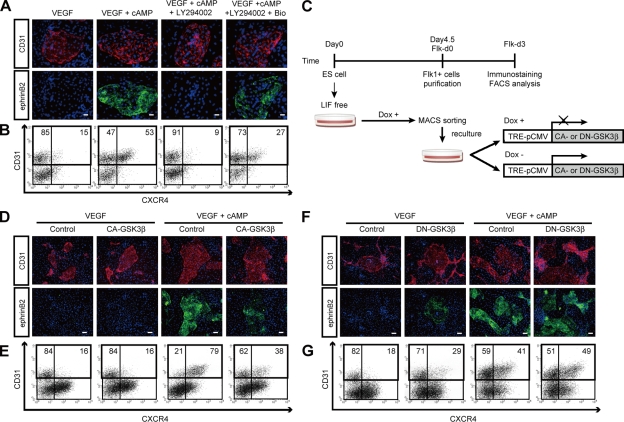
Figure 2.
Inhibitory effect of GSK3β on arterial EC differentiation. (A) Double-fluorescent staining for CD31 and ephrinB2 at Flk-d3. Top panels, CD31 (pan-ECs, red) and DAPI (blue). Bottom panels, EphB4-Fc (ephrinB2+ arterial ECs, green) and DAPI (blue). Flk1+ cells stimulated with VEGF alone (50 ng/ml), VEGF and 8bromo-cAMP (0.5 mM), VEGF, 8bromo-cAMP, and LY294002 (7.5 µM), or VEGF, 8bromo-cAMP, LY294002, and a GSK3β inhibitor, Bio (100 nM). Bars: 100 µm. (B) Flow cytometry for CD31 and CXCR4 expression at Flk-d3. Percentages of CXCR4+/CD31+ arterial ECs and CXCR4−/CD31+ venous ECs in total ECs (CD31+ cells) are indicated. (C) Experimental system for GSK3β expression. ES cell line expressing constitutive active (CA) form or dominant-negative (DN) form of GSK3β by tetracycline-inducible expression system (Tet-Off) were established. Doxycycline (Dox) was added during the first 4.5 d of culture of ES cell differentiation to Flk1+ cells. Subsequently, Flk1+ cells were sorted by MACS and plated on type IV collagen-coated dishes, and cells were cultured in the presence or absence of 1 µg/ml Dox. (D and E) Induction of CA-GSK3β. (F and G) Induction of DN-GSK3β. (D and F) Double-fluorescent staining for CD31 and ephrinB2 at Flk-d3. Top panels, CD31 (pan-ECs, red) and DAPI (blue). Bottom panels, EphB4-Fc (ephrinB2+ arterial ECs, green) and DAPI (blue). Flk1+ cells were cultured with VEGF alone, or VEGF and 8bromo-cAMP, in the presence or absence of Dox. Bars: 200 µm. (E and G) Flow cytometry for CD31 and CXCR4 expression at Flk-d3. Percentages of CXCR4+/CD31+ arterial ECs and CXCR4−/CD31+ venous ECs in total ECs (CD31+ cells) are indicated.